奥米加-3 脂肪酸:健康益处、来源和用法!
Omega-3 fatty acids are key nutrients your body needs but can’t make on its own. These essential fats play crucial roles in your brain function, and eye health, and help reduce inflammation throughout your body. You can find omega-3s in fatty fish, nuts, and seeds.
In today’s fast-paced world, many people don’t get enough omega-3s in their diet. This lack can impact your health in various ways. Eating more omega-3-rich foods or taking supplements can help fill this nutritional gap. The main types of omega-3s are ALA, EPA, and DHA. Each type has different effects on your body.
Your body needs a balance of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Most modern diets have too much omega-6 and not enough omega-3. By adding more omega-3s to your meals, you can improve this balance. This shift may lead to better heart health, sharper brain function, and reduced inflammation in your body.
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?

Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fat that your body needs to function properly. They are considered essential fatty acids because your body can’t make them on its own.
There are three main types of omega-3s:
- ALA(α-亚麻酸)
- EPA(二十碳五烯酸)
- DHA(二十二碳六烯酸)
ALA is found in plant oils, while EPA and DHA are commonly found in fish and other seafood.
Your body uses omega-3s as building blocks for cell membranes. They play a crucial role in brain function and eye health.
Omega-3s are part of a larger group called polyunsaturated fatty acids. These fats have multiple double bonds in their chemical structure, which gives them unique properties.
You can get omega-3s from your diet or through supplements. Good food sources include:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- 亚麻籽
- 奇亚籽
- 核桃
Getting enough omega-3s in your diet is important for overall health. They may help reduce inflammation and lower your risk of certain chronic diseases.
Importance of Omega-3 in Modern Diets
Omega-3 fatty acids play a crucial role in your health. They are essential fats your body can’t produce on its own. You must get them from food or supplements.
Modern diets often lack sufficient omega-3s. This imbalance can lead to health issues. Your body needs omega-3s to function properly.
These fats help reduce inflammation in your body. They support heart and brain health. Omega-3s are also important for eye function and fetal development.
The omega-6 to omega-3 ratio is key. Many people consume too many omega-6 fats compared to omega-3s. This can increase inflammation in your body.
To improve your omega-3 intake, eat more:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel)
- 核桃
- Flax seeds
- Leafy green vegetables
Omega-3s are a type of unsaturated fat. They’re healthier than saturated fats found in many processed foods. Replacing saturated fats with omega-3s can benefit your health.
Be mindful of oxidation when storing omega-3-rich foods. Proper storage helps maintain their benefits. Keep nuts and seeds in cool, dark places.
Adding omega-3s to your diet is simple. Try having fish twice a week. Sprinkle ground flax seeds on your meals. Snack on walnuts. Small changes can make a big difference in your omega-3 intake.
Types of Omega-3 Fatty Acids

Omega-3 fatty acids come in three main forms. Each type plays a unique role in your body and can be found in different food sources.
ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid)
ALA is a plant-based form of omega-3. You can find it in foods like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. Your body can’t make ALA on its own, so you need to get it from your diet.
ALA has 18 carbon atoms in its structure. While beneficial, your body must convert ALA to EPA and DHA to use it effectively. This conversion process isn’t very efficient in humans.
EPA (二十碳五烯酸)
EPA is a marine omega-3 found mainly in fatty fish. It has 20 carbon atoms and is known for its anti-inflammatory properties.
EPA plays a key role in heart health and brain function. You can get EPA by eating fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines. If you don’t eat fish often, you might consider a fish oil supplement.
DHA (二十二碳六烯酸)
DHA, like EPA, is a marine omega-3. It has 22 carbon atoms and is crucial for brain development and function.
DHA is especially important during pregnancy and early childhood. It’s found in high amounts in your brain and eyes. You can get DHA from fish sources similar to EPA.
Some algae also produce DHA, making it a good option for vegetarians and vegans.
Key Health Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids offer numerous health advantages for your body and mind. These essential nutrients can positively impact various aspects of your well-being, from supporting heart function to enhancing cognitive abilities.
心脏健康
Omega-3s play a crucial role in maintaining your cardiovascular health. They can help lower triglyceride levels and reduce blood pressure. These fatty acids also decrease the risk of arrhythmias and slow the buildup of plaque in your arteries.
Regular consumption of omega-3s may lower your chances of heart disease and stroke. They can improve the function of blood vessels and reduce harmful inflammation in your cardiovascular system.
To boost your heart health, try incorporating fatty fish like salmon or mackerel into your diet twice a week. Plant-based sources such as flaxseeds and chia seeds are also beneficial.
Brain Health and Cognitive Function
Omega-3s are essential for your brain’s structure and function. They support cognitive development throughout life, from infancy to old age.
DHA, a type of omega-3, is a major component of brain cell membranes. It helps improve communication between brain cells, enhancing memory and learning abilities.
Regular intake of omega-3s may help:
- Slow cognitive decline in older adults
- Improve focus and attention
- Enhance problem-solving skills
Studies suggest that omega-3s might lower the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. They can also support brain health during pregnancy and early childhood.
眼睛健康
Omega-3 fatty acids are crucial for maintaining your eye health. DHA is a major structural component of your retina, the part of your eye that senses light.
Getting enough omega-3s may help prevent macular degeneration, a leading cause of vision impairment and blindness in older adults. These fatty acids can also reduce the risk of dry eye syndrome.
Regular consumption of omega-3-rich foods like fatty fish can support your overall eye health. They may help protect against age-related eye diseases and maintain sharp vision as you age.
Inflammation Reduction
Omega-3s have powerful anti-inflammatory properties. They can help reduce chronic inflammation in your body, which is linked to many health problems.
These fatty acids work by:
- Decreasing the production of inflammatory compounds
- Increasing the production of anti-inflammatory molecules
By reducing inflammation, omega-3s may help prevent or manage conditions like:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Asthma
Including omega-3-rich foods in your diet can support your body’s natural anti-inflammatory processes. This may lead to better overall health and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Mental Health Benefits
Omega-3 fatty acids play a crucial role in supporting your mental well-being. They are essential for proper brain function and can influence mood and behavior.
Research suggests that omega-3s may help:
- Reduce symptoms of depression
- Alleviate anxiety
- Improve overall mood
These fatty acids are involved in producing neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that regulate mood. Low levels of omega-3s have been linked to an increased risk of psychiatric disorders.
Regular consumption of omega-3-rich foods or supplements may help manage symptoms of depression and anxiety. They can also support emotional stability and mental clarity.
Joint Health and Arthritis Relief
Omega-3 fatty acids can significantly benefit your joint health. Their anti-inflammatory properties make them particularly useful in managing arthritis symptoms.
These fatty acids may help:
- Reduce joint pain and stiffness
- Improve joint mobility
- Decrease the need for anti-inflammatory medications
For people with rheumatoid arthritis, omega-3s can help alleviate morning stiffness and tender joints. They may also slow the progression of the disease.
Including omega-3-rich foods in your diet or taking supplements can support overall joint health. This can lead to improved mobility and quality of life, especially as you age.
Skin Health and Anti-Aging
Omega-3 fatty acids play a vital role in maintaining healthy skin. They are a crucial component of your skin’s structure and can help keep it supple and moisturized.
These fatty acids may:
- Protect against sun damage
- Reduce inflammation in skin conditions like acne or psoriasis
- Support skin hydration and elasticity
Regular intake of omega-3s can help slow the aging process of your skin. They may reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles by supporting skin cell function.
Consuming omega-3-rich foods or using skincare products containing these fatty acids can promote a healthy, youthful complexion.
Weight Management and Metabolism Support
Omega-3 fatty acids can aid in your weight management efforts. They may help boost your metabolism and promote fat burning.
These fatty acids can:
- Reduce hunger and appetite
- Increase feelings of fullness
- Support fat oxidation
Omega-3s may also help improve insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight. They can support the function of metabolic organs like the liver and pancreas.
Including omega-3-rich foods in a balanced diet can support your weight loss or maintenance goals. These fatty acids may help you feel satisfied with smaller portions and reduce cravings for unhealthy foods.
Best Natural Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids

Omega-3 fatty acids are vital for your health. You can find them in many foods from both animal and plant sources. Let’s look at some of the best natural ways to get these healthy fats in your diet.
Fatty Fish
Fatty fish are top sources of omega-3s. They contain two key types: EPA and DHA. Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and herring are excellent choices. These fish are rich in omega-3s and offer other nutrients too.
You can also try anchovies. They’re small but packed with omega-3s. Canned options make it easy to add these fish to your meals.
Cod liver oil is another good source. It comes from the livers of cod fish. This oil is very high in omega-3s and vitamin D.
Plant-Based Omega-3 Sources
If you don’t eat fish, you can still get omega-3s from plants. These sources mainly provide ALA, a type of omega-3.
Walnuts are a great choice. They’re easy to add to many foods. Flaxseeds and chia seeds are also high in omega-3s. You can sprinkle them on yogurt or add them to smoothies.
Hemp seeds are another option. They’re rich in omega-3s and protein. You can use them like other seeds in your meals.
Some plant oils are good sources too. Try flaxseed oil or soybean oil. These oils work well in salad dressings.
Seafood and Algae
Oysters are a tasty way to get omega-3s. They’re also high in zinc and vitamin B12. Other shellfish like mussels and clams contain omega-3s too.
Algae is a unique source of omega-3s. It’s where fish get their omega-3s from. You can find algae oil supplements if you don’t eat seafood.
Grass-fed animals provide some omega-3s. Their meat and dairy have more omega-3s than grain-fed animals. Choose grass-fed beef or dairy for a boost in omega-3s.
Omega-3 Supplements: What You Need to Know
Omega-3 supplements offer a convenient way to boost your intake of these essential fatty acids. They come in various forms and have different benefits and considerations.
鱼油保健品
鱼油 is a popular omega-3 supplement. It contains two key omega-3s: EPA and DHA. These fatty acids support heart and brain health.
Fish oil comes in capsules or liquid form. Capsules are easy to take, while liquid offers flexible dosing.
When choosing a fish oil, look for products that list the amount of EPA and DHA. A typical dose is 250-500 mg combined EPA and DHA per day.
Some people worry about mercury in fish oil. Good news – most fish oil supplements are purified to remove contaminants.
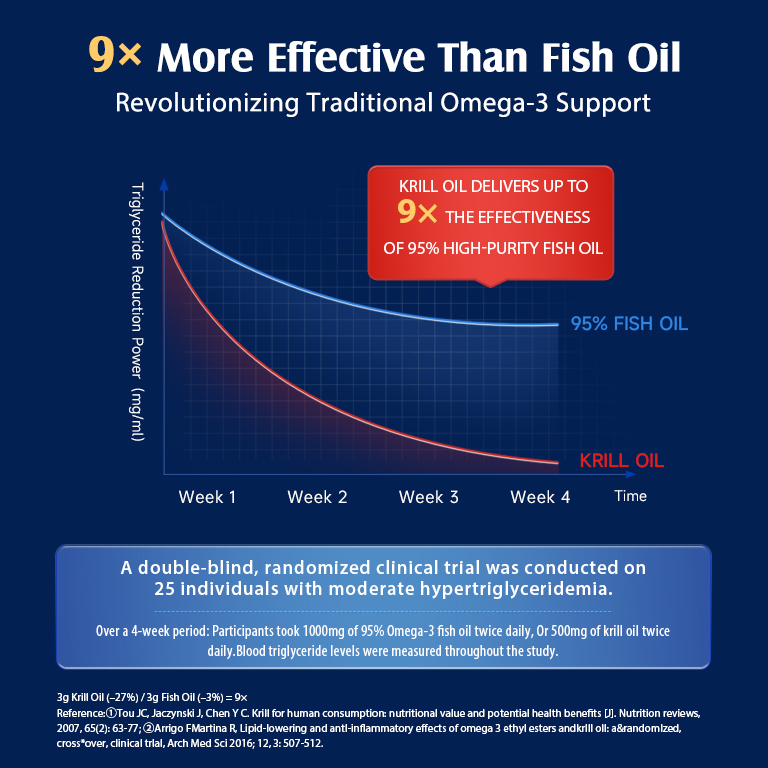
Krill Oil vs. Fish Oil
Krill oil is another source of omega-3s. It comes from tiny crustaceans called krill.
Krill oil has some unique features:
- It contains omega-3s in a form that may be easier for your body to use
- It includes astaxanthin, an antioxidant
- It may cause less “fishy” burps than fish oil
However, krill oil is often more expensive than fish oil. It also typically contains lower amounts of EPA and DHA per capsule.
Both can be good choices. Your decision may depend on your budget and personal preferences.
Vegan and Vegetarian Omega-3 Supplements
If you don’t eat fish, you can still get omega-3s from supplements. Algae oil is a popular vegan option.
Algae oil contains DHA and sometimes EPA. It’s the same source that fish get their omega-3s from.
Other plant-based options include:
- Flaxseed oil
- Chia seed oil
- Hemp seed oil
These contain ALA, a type of omega-3. Your body can convert some ALA to EPA and DHA, but not very efficiently.
If you’re vegan or vegetarian, algae oil is often the best choice for getting EPA and DHA directly.
Selecting High-Quality Supplements
Choosing a good omega-3 supplement can be tricky. Here are some tips:
- Check for third-party testing. Look for seals from USP, NSF, or ConsumerLab.
- Read the label carefully. Look for the amount of EPA and DHA, not just “fish oil.”
- Consider the form. Triglyceride forms may be better absorbed than ethyl esters.
- Look for freshness. A good supplement should have minimal fishy taste or smell.
- Check for added ingredients. Some products include vitamin D or other nutrients.
Remember, omega-3 supplements aren’t a replacement for a healthy diet. They work best as part of an overall healthy lifestyle.
How Much Omega-3 Do You Need?
The amount of omega-3 you need varies based on several factors. Getting the right balance is key for your health and well-being.
Recommended Daily Intake
Adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acids differs by age and gender. For adults, the recommended amount is:
- Men: 1.6 grams per day
- Women: 1.1 grams per day
Pregnant women need 1.4 grams daily, while breastfeeding women require 1.3 grams. These amounts can be met through diet or supplements.
Eating fatty fish twice a week can help you reach these goals. Good options include:
- 三文鱼
- 鲭鱼
- 沙丁鱼
- Trout
If you don’t eat fish often, consider taking an omega-3 supplement.
Factors That Influence Omega-3 Needs
Your omega-3 needs may change based on certain factors:
- Age: Older adults might need more omega-3s to support brain health.
- Health conditions: People with heart disease may benefit from higher doses.
- Diet: Vegetarians and vegans may need to pay extra attention to their intake.
- Pregnancy: Expecting mothers need more omega-3s for fetal development.
- Activity level: Athletes might require higher amounts for recovery.
Always talk to your doctor before changing your omega-3 intake. They can help you determine the right amount for your specific needs.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of Omega-3 Intake
Omega-3 fatty acids offer many health benefits, but they can also cause some unwanted effects. You should be aware of possible side effects and risks, especially if you take high doses.
常见副作用
When you start taking omega-3 supplements, you might notice some mild side effects. These can include bad breath, nausea, and headaches. You may also experience:
- Fishy burps or taste in your mouth
- Stomach discomfort or bloating
- 腹泻
- 胃灼热
These effects are usually not serious. You can reduce them by taking supplements with meals or freezing them before use. If side effects persist, talk to your doctor.
Risks of Excessive Omega-3
Taking too much omega-3 can lead to more serious issues. High doses may:
- Increase bleeding risk, especially if you take blood thinners
- Raise your LDL cholesterol (the “bad” cholesterol)
- Lower your immune function
Be careful with omega-3 supplements if you have a seafood allergy. Some people may experience an allergic reaction.
While omega-3s can help lower triglycerides, too much may affect blood sugar control in people with diabetes. Always consult your doctor before starting high-dose omega-3 supplements, especially if you have health conditions or take medications.
Omega-3 for Special Populations
Omega-3 fatty acids play a crucial role in different life stages. They are especially important for pregnant women, children, and older adults. These groups have unique needs that omega-3s can help address.
Pregnancy and Nursing
During pregnancy and nursing, omega-3 fatty acids are vital for fetal and infant development. They support brain growth and eye health in babies.
Pregnant women need more DHA, a type of omega-3. It helps form the baby’s brain and retina. You can get DHA from fatty fish or supplements.
For breastfeeding women, omega-3s pass through breast milk to the baby. This helps with the child’s ongoing brain development. Aim for 2-3 servings of low-mercury fish per week if you’re pregnant or nursing.
Omega-3s for Children
Children also benefit from omega-3s. They support brain function and may help with ADHD symptoms.
Some studies suggest omega-3s might improve focus in kids with ADHD. They may also boost learning and memory in all children.
Good sources for kids include:
- Fatty fish (salmon, tuna)
- 核桃
- 亚麻籽
- Omega-3 fortified foods
If your child doesn’t like fish, talk to your doctor about supplements.
Elderly Population
As you age, omega-3s remain important. They may help protect brain health and reduce inflammation.
Omega-3s might lower the risk of age-related cognitive decline. Some studies suggest they could help prevent Alzheimer’s disease.
For heart health, omega-3s can be beneficial. They may help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Aim for at least two servings of fatty fish per week. If you can’t eat fish, consider taking a high-quality omega-3 supplement.
Omega-3 and Disease Prevention
Omega-3 fatty acids play a crucial role in preventing various diseases. These essential fats help protect your body against inflammation and oxidative stress, which are key factors in many chronic conditions.
Cardiovascular Disease
Omega-3 fatty acids can benefit cardiovascular health in several ways. They help lower triglycerides, reduce blood pressure, and decrease the risk of arrhythmias.
Omega-3s may also:
- Slow the buildup of plaque in your arteries
- Reduce the chance of heart attacks and strokes
- Lower your risk of sudden cardiac death
Studies show that eating fish rich in omega-3s twice a week can cut your risk of dying from heart disease by up to 36%. If you don’t eat fish, consider taking a high-quality omega-3 supplement.
Type 2 Diabetes
Omega-3 fatty acids can help manage type 2 diabetes and its complications. They improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation, both key factors in diabetes.
Benefits for people with diabetes include:
- Better blood sugar control
- Reduced risk of heart disease
- Improved kidney function
A diet rich in omega-3s may even help prevent type 2 diabetes. Aim to include fatty fish like salmon or sardines in your meals twice a week.
Cancer Prevention
Omega-3 fatty acids show promise in cancer prevention. They may help slow the growth of cancer cells and reduce inflammation linked to cancer development.
Potential benefits include:
- Lower risk of colon cancer
- Reduced chance of prostate cancer
- Possible protection against breast cancer
While more research is needed, including omega-3-rich foods in your diet is a smart choice for overall health and potential cancer prevention.
Autoimmune Diseases
Omega-3s can help manage autoimmune diseases by reducing inflammation and regulating immune function. They may be beneficial for conditions like:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Lupus
- Multiple sclerosis
In rheumatoid arthritis, omega-3s can decrease joint pain and stiffness. For lupus, they may help reduce inflammation and improve symptoms.
Adding more omega-3s to your diet through fatty fish or supplements may help manage your autoimmune condition. Always talk to your doctor before starting any new supplement regimen.
Omega-3s in Popular Diets

Many popular diets include foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These diets recognize the importance of omega-3s for health. Different approaches emphasize various omega-3 sources.
Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet strongly features omega-3s. It includes plenty of fatty fish like mackerel and sardines. You’ll also find olive oil, nuts, and seeds on the menu.
This diet balances omega-3s with other healthy fats. You’ll eat fish at least twice a week. Plant sources of omega-3s are common too. Think walnuts, flaxseeds, and leafy greens.
The Mediterranean approach isn’t just about omega-3s. It’s a lifestyle that includes whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. This mix provides a wide range of nutrients alongside omega-3s.
Paleo and Keto Diets
Paleo and keto diets often include good omega-3 sources. Both emphasize foods like fatty fish. You might eat salmon, trout, or mackerel regularly.
These diets also include eggs from pasture-raised hens. These eggs have higher omega-3 content. Nuts and seeds are common in paleo diets, adding more omega-3s.
Keto dieters might use fish oil supplements. This helps balance their fat intake. Both diets limit processed foods. This means you avoid unhealthy fats that can outweigh omega-3 benefits.
Plant-Based Diets
Plant-based diets can provide omega-3s too. You’ll focus on ALA, a type of omega-3 found in plants. Good sources include flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts.
Algae oil is a great option for DHA and EPA. These are the omega-3s usually found in fish. You can find algae oil supplements or foods fortified with it.
Some plant-based eaters use omega-3 supplements. This ensures they get enough EPA and DHA. Eating a variety of omega-3 rich plants helps too. Include seeds, nuts, and leafy greens in your meals.
常见问题
Omega-3 fatty acids play a crucial role in human health. Many people have questions about their benefits, sources, and proper usage. Let’s explore some common inquiries about these essential nutrients.
What are the health benefits associated with consuming omega-3 fatty acids?
Omega-3s support heart health by lowering blood pressure and reducing triglycerides. They also help brain function and may reduce inflammation in your body.
These fatty acids are important for eye health and fetal development during pregnancy.
Which specific foods are rich in omega-3 fatty acids for vegetarians?
Vegetarians can get omega-3s from plant sources. Flaxseed is a good option, providing alpha-linolenic acid (ALA).
Chia seeds, walnuts, and hemp seeds are also rich in ALA. You can find omega-3 fortified foods like certain brands of eggs, yogurt, and milk.
How does regular intake of omega-3 fatty acids affect women’s health?
For women, omega-3s may help reduce menstrual pain. They’re vital during pregnancy for fetal brain and eye development.
Omega-3s might also help with mood regulation and could lower the risk of depression.
Are there recommended daily dosages of omega-3 for adults, and how are they determined?
There’s no set recommended daily allowance for omega-3s. The amount you need depends on your age, sex, and health status.
Most health organizations suggest 250-500 mg of combined EPA and DHA per day for healthy adults.
What should be considered when choosing omega-3 fatty acid supplements?
Look for supplements that contain both EPA and DHA. Check the amount of omega-3s per serving, not just the total oil amount.
Consider the form of omega-3. Fish oil is common, but krill oil is another option. Choose a reputable brand and look for third-party testing.
Are there any groups of people who should avoid taking omega-3 supplements?
People with fish or shellfish allergies should be cautious with marine-sourced omega-3s. Those on blood-thinning medications should consult their doctor before taking omega-3 supplements.
If you’re scheduled for surgery, you might need to stop taking omega-3s temporarily. Always talk to your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement.
结论
Omega-3 fatty acids are key for your long-term health. They support your heart, brain, and overall well-being.
Adding omega-3 to your diet is easy. You can eat fatty fish like salmon or sardines twice a week. If you don’t like fish, try walnuts, chia seeds, or flaxseeds.
Omega-3 supplements are another option. Fish oil capsules are common, but algae-based supplements work too. These are good for vegetarians and vegans.
Cooking with omega-3-rich oils like flaxseed oil can boost your intake. You can also add ground flaxseed to smoothies or oatmeal.
Remember, consistency is key. Make omega-3 foods part of your regular meals. Small, daily changes can have big health benefits over time.
Talk to your doctor before starting any new supplement. They can help you find the right amount for your needs.
By making omega-3 a priority, you’re investing in your health. It’s a simple step that can pay off in many ways as you age.