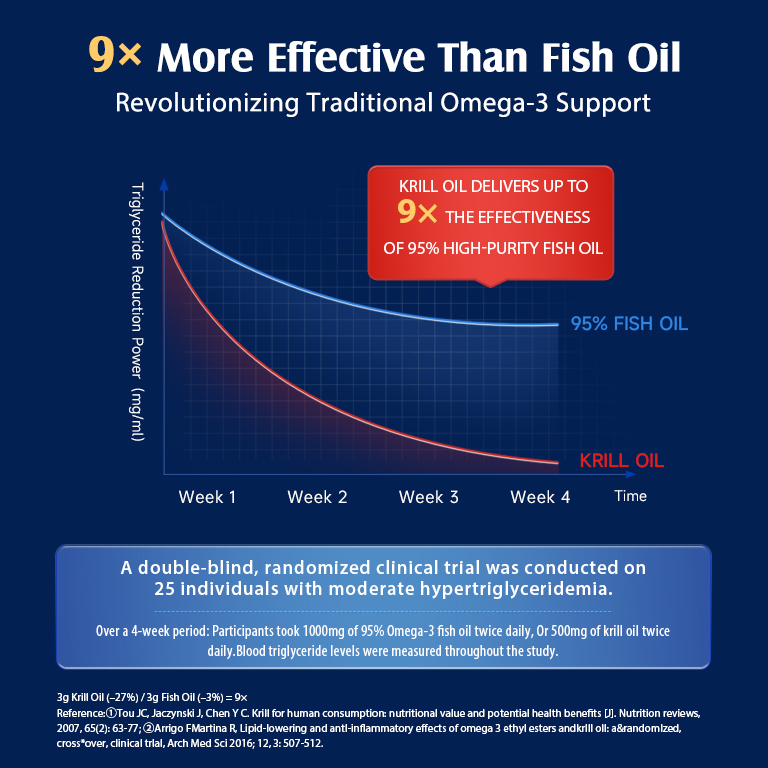
Krill Oil vs Fish Oil: Comparing Omega-3 Sources for Health Benefits.
Krill oil and fish oil are popular omega-3 supplements. Both come from sea creatures but have key differences. You may wonder which is better for your health.
Krill oil and fish oil both provide omega-3 fatty acids that can support heart health, but krill oil may be absorbed more easily by your body. Fish oil typically has more omega-3s per serving. The amount varies between products.
Krill oil comes from tiny shrimp-like creatures, while fish oil comes from fatty fish. Krill oil contains a substance called astaxanthin that gives it a reddish color. This acts as an antioxidant. Both oils may help reduce inflammation in your body. When choosing between them, consider factors like price, sustainability, and how well you tolerate each type.
Understanding Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats your body needs for many important functions. They play key roles in brain health, heart health, and reducing inflammation.
Roles in the Body
Omega-3s help form cell membranes throughout your body. They provide energy and support your heart, blood vessels, lungs, and immune system.
EPA and DHA are especially important for brain function and development. They may help improve memory and reduce the risk of cognitive decline as you age.
These fatty acids also have anti-inflammatory effects. This can help reduce your risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and arthritis.
Omega-3s support eye health and may lower the risk of macular degeneration. They’re also crucial during pregnancy for fetal brain and eye development.
Sources of Omega-3s
You can get omega-3s from both food and supplements. The main types are ALA, EPA, and DHA.
ALA is found in plant oils like flaxseed, soybean, and canola oil. Your body can convert some ALA to EPA and DHA, but the process isn’t very efficient.
EPA and DHA come mainly from fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines. You can also get them from fish oil supplements.
Krill oil is another source of EPA and DHA. It may be easier for your body to absorb compared to fish oil.
Algae-based supplements are a good option for vegetarians and vegans. They provide DHA and sometimes EPA.
Comparing Krill Oil and Fish Oil
Krill oil and fish oil both offer omega-3 fatty acids, but they differ in key ways. Their composition, how well your body absorbs them, and environmental impacts set them apart.
Composition and Nutrients
Krill oil contains omega-3s attached to phospholipids, while fish oil has omega-3s in triglyceride form. This difference affects how your body processes each oil.
Krill oil also provides astaxanthin, a powerful antioxidant. Fish oil lacks this compound.
Both oils supply EPA and DHA, crucial omega-3 fatty acids. However, fish oil typically offers higher amounts per serving.
Here’s a quick comparison:
- Krill oil: Phospholipid-bound omega-3s, astaxanthin
- Fish oil: Triglyceride-bound omega-3s, higher EPA/DHA content
Bioavailability and Absorption

Your body may absorb krill oil more easily than fish oil. The phospholipid structure in krill oil helps it mix with your stomach contents better.
This improved mixing can lead to the following:
- Faster absorption
- Less “fishy” aftertaste
- Reduced risk of digestive issues
Fish oil, while still beneficial, may not be absorbed as quickly. You might need larger doses to get the same effect as krill oil.
Sustainability and Contamination
Krill oil comes from tiny Antarctic crustaceans. The krill population is vast, making it a more sustainable choice than some fish oil sources.
Fish oil sustainability varies based on the fish species used. Some sources face overfishing concerns.
Contamination is another factor to consider:
- Krill live in cleaner Antarctic waters, reducing pollution risks.
- Fish can accumulate more toxins, but high-quality fish oils undergo purification.
Both oils can be safe and eco-friendly if you choose reputable brands. Look for third-party testing and sustainable harvesting practices when selecting either supplement.
Health Benefits of Omega-3 Supplementation
Omega-3 fatty acids offer several health benefits when taken as supplements. They can improve heart health, reduce inflammation, and support brain function.

Cardiovascular Health
Omega-3 supplements may lower the risk of heart disease. They can help reduce high triglyceride levels in your blood. This is important because high triglycerides are linked to heart problems.
Omega-3s can also improve your cholesterol profile. They may increase HDL (good) cholesterol while lowering LDL (bad) cholesterol. This balance is crucial for heart health.
These supplements might help lower blood pressure too. Even a small reduction in blood pressure can significantly decrease your risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Inflammatory Conditions and Arthritis
Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties. This makes them useful for managing various inflammatory conditions.
If you have rheumatoid arthritis, omega-3s may help reduce joint pain and stiffness. They can also decrease the need for anti-inflammatory medications in some cases.
For other inflammatory conditions, like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, omega-3s might help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract. This can lead to symptom relief and improved quality of life.
Brain and Cognitive Health
Omega-3s play a crucial role in brain health. They are essential for the structure and function of brain cells.
Taking omega-3 supplements may improve memory and cognitive function. This is especially important as you age, as it might help slow cognitive decline.
Some studies suggest omega-3s could help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. They may also support better mood overall.
For pregnant women, omega-3s are vital for fetal brain development. Adequate intake during pregnancy may lead to better cognitive outcomes in children.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
Taking krill oil or fish oil supplements can have some risks. It’s important to know about possible side effects and factors to keep in mind before using these products.
Interaction with Medications
Krill and fish oils can interact with blood-thinning medicines. If you take anticoagulants like warfarin, talk to your doctor before starting these supplements. They may increase bleeding risk.
These oils can also affect blood sugar levels. If you have diabetes or take medications that lower blood sugar, monitor your levels closely when using krill or fish oil.
Some people report digestive issues when taking these supplements. Start with a low dose and increase slowly to reduce stomach upset.
Allergies and Sensitivities
If you have a shellfish allergy, avoid krill oil. It comes from tiny crustaceans and may trigger an allergic reaction.
Fish oil can cause a fishy aftertaste or fishy burps. This is more common with lower-quality products. Try taking the capsules with meals or freezing them to reduce this effect.
Some people experience skin rashes or itching when taking fish or krill oil. If you notice any allergic symptoms, stop using the supplement and consult your doctor.
Oxidation and Rancidity
Both krill and fish oils can go rancid if not stored properly. Rancid oils taste bad and may be harmful to your health.
To prevent oxidation:
- Keep supplements in a cool, dark place
- Check the expiration date before use
- Look for products with added antioxidants like vitamin E
If your supplements smell off or taste very fishy, they may have gone bad. Throw them out and get a fresh bottle.
Krill oil may be less prone to oxidation than fish oil due to its antioxidant content. However, both need proper storage to maintain quality.
Choosing the Right Supplement for Your Diet
Picking the best omega-3 supplement depends on your diet and health needs. There are options for both fish eaters and plant-based diets. Your choice affects how well your body absorbs the nutrients.

Fish-Based vs Plant-Based Omega-3s
Fish oil comes from fatty fish like salmon and sardines. It has high levels of EPA and DHA, which are easy for your body to use. Krill oil is another fish-based choice. It may be better absorbed than regular fish oil.
For plant-based diets, flaxseed and chia seeds are good sources of omega-3s. These contain ALA, which your body must convert to EPA and DHA. This process is less efficient than getting EPA and DHA directly from fish sources.
• Fish-based options:
- Fish oil
- Krill oil
• Plant-based options:
- Flaxseed oil
- Chia seed oil
Special Dietary Considerations
If you’re vegan or vegetarian, plant-based supplements are your go-to. Algae oil is a great choice as it provides DHA directly without animal products. It’s the only plant source that offers significant amounts of DHA.
For those who eat seafood but have shellfish allergies, avoid krill oil. Stick to fish oil from sources like cod liver or salmon. If you’re following a kosher or halal diet, look for certified supplements that meet these standards.
Vegans and vegetarians should consider:
- Algae oil supplements
- Higher doses of flaxseed or chia seed oil to compensate for lower absorption
Fish eaters with dietary restrictions:
- Kosher or halal-certified fish oils
- Avoid krill oil if allergic to shellfish
Best Practices for Omega-3 Supplementation
Taking omega-3 supplements safely and effectively requires care and attention. Following proper guidelines can help you get the most benefit from krill oil or fish oil.
Consulting a Healthcare Provider
Before starting any new supplement, talk to your doctor. This is especially important if you take blood-thinning medications. Your healthcare provider can review your medical history and current medications.
They’ll help determine if omega-3 supplements are right for you. They can also suggest the best type and dose based on your needs.
If you have allergies, especially to seafood, tell your doctor. They’ll help you choose a safe option.
Regular check-ups can help monitor how the supplements affect your health. Your doctor may test your triglyceride and cholesterol levels to see if the supplements are working.
Dosage and Frequency
The right dose of omega-3s varies from person to person. It depends on factors like age, health status, and reason for taking the supplement.
A common daily dose is 250-500 mg of combined EPA and DHA. Some people may need higher doses. Always follow the instructions on the label or your doctor’s advice.
Take omega-3 supplements with food to improve absorption and reduce side effects. Spreading your dose throughout the day can also help.
Start with a lower dose and slowly increase it. This helps your body adjust and lowers the risk of side effects.
Store your supplements in a cool, dark place. Check the expiration date regularly. Old or rancid oils can be harmful.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the health benefits of krill oil over fish oil?
Krill oil may be more easily absorbed by your body than fish oil. This means you might get more omega-3 benefits from a smaller dose.
Krill oil also contains astaxanthin, an antioxidant not found in fish oil. This extra component could offer added protection against cell damage.
How does krill oil influence cholesterol levels relative to fish oil?
Krill oil may be more effective at managing cholesterol than fish oil. It can help lower bad cholesterol (LDL) while raising good cholesterol (HDL).
Fish oil also supports heart health, but krill oil’s unique structure might make it better at improving your cholesterol balance.
Can krill oil reduce joint pain more effectively than fish oil?
Both oils can help with joint pain, but krill oil might work faster. Its omega-3s are in a form that your body can use more quickly.
This could mean quicker relief from joint discomfort when you take krill oil compared to fish oil.
What are the potential risks associated with consuming krill oil?
Krill oil is generally safe, but it can cause side effects like fishy burps or upset stomach. If you’re allergic to shellfish, you should avoid krill oil.
Always talk to your doctor before starting any new supplement, especially if you take blood thinners.
In terms of cognitive function, how do krill oil and fish oil differ?
Both krill and fish oil support brain health. Krill oil’s omega-3s might reach your brain more easily due to their structure.
This could potentially make krill oil more effective for improving memory and reducing cognitive decline.
Are there anti-inflammatory benefits unique to krill oil over fish oil?
Krill oil has a special form of omega-3s that may fight inflammation better than fish oil. It also contains astaxanthin, which has extra anti-inflammatory properties.
These features might make krill oil more powerful at reducing inflammation in your body compared to fish oil.
Summary
In general, both krill oil and fish oil supplements are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids. When it comes to krill oil, it has greater bioavailability, antioxidants, and more sustainable sourcing methods for health benefits than fish oils.
However, while krill oil and fish oil supplements are good sources of omega-3 fatty acids, krill oil has more advantages than fish oil in many ways. If you are not familiar with these omega-3 supplements and want to get some omega-3 fatty acids from them, please consult with your healthcare provider or doctor before consuming them.