Omega 3-6-9 Fatty Acids: Essential Nutrients for Optimal Health!
You’ve probably heard about omega fatty acids, but do you know the difference between omega-3, omega-6, and omega-9? These essential fats play crucial roles in your body, from supporting heart health to maintaining healthy skin. While they may sound similar, each type has unique properties and food sources that can impact your overall well-being.
Omega-3, omega-6, and omega-9 fatty acids each provide distinct health benefits, with omega-3s found primarily in oily fish, omega-6s and omega-9s abundant in plant oils, nuts, and seeds. Your body cannot produce certain omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids on its own, making them “essential” nutrients you must get from your diet. However, omega-9s can be manufactured by your body when needed.
Finding the right balance of these fatty acids in your diet matters. The omega fats compete for the same enzymes in your body, making their ratio important for optimal health. Many experts suggest that modern diets contain too many omega-6s and not enough omega-3s. Adding more oily fish to your meals and being mindful of your plant oil consumption can help you achieve a healthier balance of these important nutrients.
Understanding Omega-3-6-9 Fatty Acids
Omega fatty acids play vital roles in your body’s health and function. These essential nutrients differ in their chemical structure and come from various food sources that you can easily incorporate into your diet.

Chemical Structure and Classification
Omega-3 and omega-6 are polyunsaturated fatty acids, meaning they contain multiple double bonds in their carbon chain. The number after “omega” indicates where the first double bond appears from the methyl end of the molecule.
Omega-3s have their first double bond at the third carbon atom, while omega-6s have it at the sixth. Unlike these two, omega-9 is a monounsaturated fatty acid with only one double bond at the ninth carbon position.
Your body cannot produce omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids on its own, making them essential fatty acids that you must get through your diet. In contrast, omega-9 is considered non-essential because your body can produce it naturally when needed.
Sources of Omega-3, 6, and 9
Omega-3 fatty acids are abundant in:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- Flaxseeds and flaxseed oil
- Walnuts
- Chia seeds
Omega-6 fatty acids are commonly found in:
- Vegetable oils (corn, soybean, sunflower)
- Nuts and seeds
- Poultry
- Eggs
For omega-9 fatty acids, look to:
- Olive oil
- Avocados
- Almonds
- Macadamia nuts
The typical Western diet often contains too much omega-6 and not enough omega-3. Health experts recommend improving your omega-3 to omega-6 ratio by increasing your consumption of fatty fish and reducing processed foods high in vegetable oils.
Including foods rich in all three omega fatty acids helps support brain health, skin health, and overall body function.
Health Benefits of Omega Fatty Acids
Omega fatty acids deliver powerful health benefits that support your body’s vital systems. These essential fats work in different ways to protect your heart, enhance brain function, and fight inflammation.

Cardiovascular Health
Omega-3 fatty acids significantly support your heart health by helping to lower triglycerides in the blood. This reduction is important because high triglyceride levels can contribute to heart disease.
Research shows omega-3 supplements can reduce the risk of cardiovascular death by 19% compared to placebo treatments. This protective effect may help prevent serious conditions like stroke.
Your body needs a proper balance between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Too much omega-6 can promote inflammation, while adequate omega-3 helps counteract this effect.
Key benefits for your heart include:
- Improved blood vessel function
- Reduced blood pressure
- Better cholesterol balance
- Lower risk of irregular heartbeat
Brain and Nervous System
Omega-3 fatty acids are crucial for your brain health throughout life. They form part of cell membranes in your brain and help maintain cognitive function as you age.
DHA, a type of omega-3, makes up about 40% of the polyunsaturated fatty acids in your brain. Regular consumption may help protect against Alzheimer’s disease and cognitive decline.
These essential fats support:
- Memory formation
- Learning ability
- Mood regulation
- Nervous system communication
Omega-3s help maintain the fluidity and flexibility of cell membranes in your brain. This property allows for better signaling between brain cells.
Children and pregnant women especially benefit from adequate omega-3 intake for proper brain development and function.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Omega fatty acids play important roles in controlling inflammation throughout your body. Omega-3s produce compounds that actively reduce inflammation, while some omega-6s can promote it.
The anti-inflammatory properties of omega-9s help protect your eyes, skin, liver, and intestines from excessive inflammation. This can reduce symptoms in inflammatory conditions and support overall wellness.
Your immune system functions better with proper omega balance. Inflammation reduction helps with:
- Joint pain and stiffness
- Skin conditions like eczema
- Digestive disorders
- Respiratory issues
For maximum anti-inflammatory benefits, focus on increasing your omega-3 intake while maintaining moderate levels of omega-6 and omega-9 fatty acids.
Adding omega supplements to your diet may help address imbalances when food sources are insufficient.
Role in Disease Prevention
Fatty acids play critical roles in preventing serious health conditions, particularly those related to heart health and inflammation. The types of fats you consume can significantly impact your risk factors for major diseases.
Reducing the Risk of Chronic Diseases
Omega-3 fatty acids show particularly strong effects in preventing cardiovascular disease. For people who already have coronary heart disease, omega-3 supplementation provides stronger protective benefits than for healthy individuals. These beneficial fats can lower your risk of heart problems when you include them in your regular diet.
The protective effects include:
- Reducing inflammation throughout your body
- Lowering triglyceride levels
- Decreasing blood pressure
- Improving arterial function
Omega-9 fatty acids help prevent inflammation in multiple body systems, including your eyes, skin, liver, and intestines. Olive oil, rich in omega-9s, is particularly effective for this purpose.
For both primary and secondary prevention of heart disease, fish and plant-based omega-3s can improve your lipid profile and overall cardiovascular health.
Impact on Cancer
Research suggests that omega-3 fatty acids may help reduce cancer risk through their anti-inflammatory properties. These fats can influence cell membrane composition and alter how cells respond to potential cancer triggers.
Specific cancer-fighting benefits include:
- Slowing cancer cell growth
- Reducing inflammation that can promote tumor development
- Supporting healthy cell division
EPA and DHA (types of omega-3s found in fish oil) appear particularly promising for reducing risks of certain cancers, including colorectal and breast cancers.
The balance between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids is important. Too much omega-6 relative to omega-3 may create a pro-inflammatory environment that could increase cancer risk. Maintaining a proper ratio in your diet may help protect against cancer development.
The Importance of Omega Balance
Getting the right balance of omega fatty acids in your diet affects your health in many ways. Your body needs all types of omega fats, but the proportions matter significantly for reducing inflammation and supporting overall wellness.

Ideal Omega-6/Omega-3 Ratio
Research suggests that a lower ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids is better for your health. The ideal ratio is between 1:1 and 4:1, but most Western diets have a ratio of 15:1 or higher. This imbalance happens because modern diets contain too many omega-6 fats from vegetable oils and processed foods.
Studies show that a lower omega-6/omega-3 ratio helps reduce the risk of many chronic diseases common in Western societies. To improve your ratio, you can:
- Increase omega-3 rich foods (fatty fish, flaxseeds, walnuts)
- Reduce processed foods containing vegetable oils
- Choose olive oil (contains omega-9) over corn or soybean oils
- Consider fish oil supplements if your diet lacks omega-3s
Consequences of Imbalance
When your omega fatty acid balance tips too far toward omega-6, inflammation in your body can increase. This chronic inflammation contributes to several health problems, including heart disease through a process called atherogenesis (plaque buildup in arteries).
An imbalanced ratio may affect your:
- Cardiovascular health: Higher risk of blood clots and arterial inflammation
- Immune function: Overactive inflammatory responses
- Joint health: Increased pain and inflammation
- Skin condition: More inflammatory skin issues
The good news is that both omega-3 and omega-6 fats are beneficial when consumed in the right proportions. Omega-6 fats help lower harmful LDL cholesterol while omega-3s and omega-9s reduce inflammation in various body tissues.
Dietary Sources
Omega fatty acids come from different foods in your diet. The right balance of omega-3, omega-6, and omega-9 fatty acids is important for your health.
Plant-Based Sources
Plants offer several excellent sources of omega fatty acids. Flaxseed contains high amounts of alpha-linolenic acid, an omega-3 fatty acid that your body can convert to other beneficial omega-3s. Just one tablespoon of flaxseed oil provides about 7 grams of omega-3s.
Walnuts are rich in omega-6 fatty acids, containing about 37 grams per 100 grams. Other nuts like almonds contain around 12 grams of omega-6 per 100 grams.
For omega-9 fatty acids, olive oil is an excellent source. Unlike omega-3 and omega-6, your body can produce omega-9 fatty acids, but consuming them in foods like olive oil still offers health benefits.
Other plant sources include:
- Chia seeds (omega-3)
- Hemp seeds (omega-3 and omega-6)
- Avocados (omega-9)
- Sunflower seeds (omega-6)
Marine Sources
Seafood provides the most easily used forms of omega-3 fatty acids. Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and anchovies are all rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These contain EPA and DHA, which your body doesn’t need to convert before use.
Sardines are particularly valuable as they’re widely available, affordable, and contain fewer contaminants than larger fish. Just 100 grams of sardines provides about 1.5 grams of omega-3 fatty acids.
Fish oil supplements offer concentrated omega-3s when you don’t consume enough seafood. A typical fish oil supplement contains about 1,000 mg of fish oil with 180 mg EPA and 120 mg DHA.
Other marine sources include:
- Oysters
- Herring
- Trout
- Seaweed and algae (good for vegetarians)
Supplementation and Recommendations
Many people choose omega-3-6-9 supplements to improve their fatty acid intake. However, most healthy individuals can get adequate amounts through diet alone, while some specific health conditions may benefit from targeted supplementation.
When to Consider Supplements
You should consider omega supplements if your diet lacks fatty fish or plant sources of these essential nutrients. People with cardiovascular health concerns may benefit from EPA and DHA supplements. Those with inflammatory conditions or cognitive concerns might also find omega-3 supplements helpful.
Fish oil is the most common source of EPA and DHA, while flaxseed oil provides ALA. If you follow a vegetarian or vegan diet, algal oil supplements offer a plant-based source of DHA.
Most people don’t need omega-6 or omega-9 supplements since these are abundant in the typical diet. In fact, the average person consumes too much omega-6 relative to omega-3.
Children with certain behavioral concerns may benefit, as research shows that omega-3-6-9 supplementation may help with anxious and depressed behaviors.
Dosage and Safety
For general health, most experts recommend 250-500mg combined EPA and DHA daily. Higher therapeutic doses (1-4g daily) should only be taken under medical supervision.
Common Omega-3 Sources:
- Fish oil capsules: 1000mg (typically containing 180mg EPA and 120mg DHA)
- Algal oil: 300-900mg DHA per serving
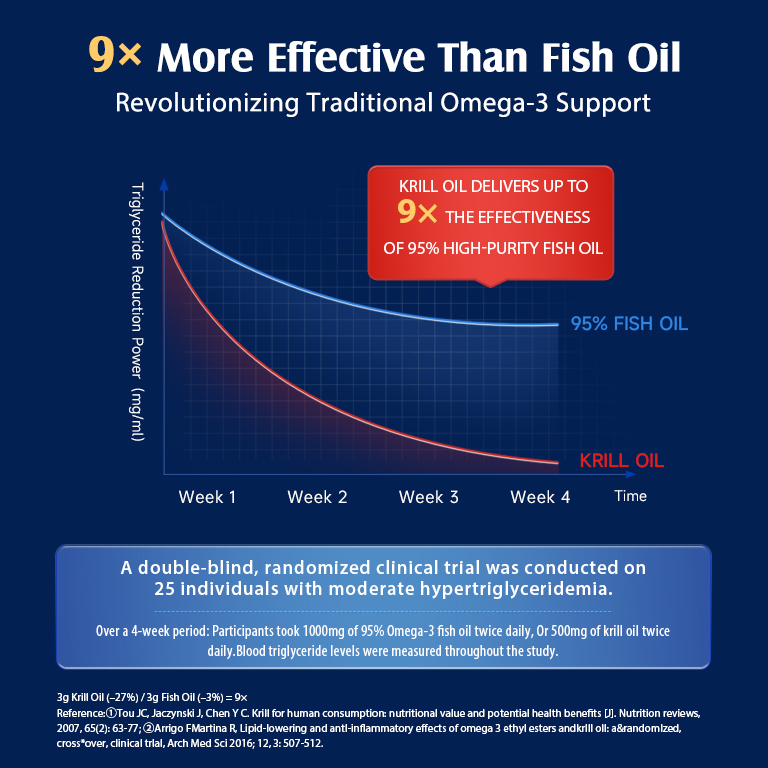
- Krill oil: Similar to fish oil but often better absorbed
Most omega-3 supplements are safe when taken as directed, but excessive amounts may increase bleeding risk or interact with blood-thinning medications.
Side effects are usually mild and may include a fishy aftertaste, bad breath, heartburn, or digestive discomfort. Taking supplements with meals can reduce these effects.
Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any supplement, especially if you have existing health conditions or take medications.
Omega Fatty Acids and Metabolism
Omega fatty acids play crucial roles in your body’s metabolic processes. These essential fats are involved in energy production and cellular function, with each type offering unique benefits to your metabolic health.
Role in Energy Production
When you consume foods rich in omega fatty acids, your body must first break them down before using them. Fatty acids are hydrolyzed from dietary fats like triglycerides in your small intestine before absorption can occur. This process is essential for proper utilization.
Your body can release essential fatty acids from adipose tissue during periods of dietary-fat restriction or malabsorption, especially when facing an energy deficit. This mechanism helps maintain vital functions even when intake is low.
Omega-3 fatty acids—particularly ALA, EPA, and DHA—support metabolic health in unique ways. ALA must be converted by your body into the more active EPA and DHA forms, though this conversion process isn’t very efficient.
Omega-6 fatty acids like LA are also important to cell membrane structure and function, helping your cells respond properly to metabolic demands.
The balance between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids affects your metabolic processes significantly. Most people consume plenty of omega-6 but not enough omega-3 fatty acids, which can impact energy production and cellular health.
Impact on Skin Health
Omega-3 fatty acids offer impressive benefits for your skin. They can regulate oil production and improve balanced hydration in your skin, helping maintain a healthy complexion.
When you consume enough omega-3s, you may notice your skin becomes more resilient. These fatty acids are particularly effective at accelerating wound healing and supporting your skin’s repair processes.
Inflammation is a common factor in many skin conditions. Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce symptoms of inflammatory skin diseases like psoriasis and atopic dermatitis.
You might not know that omega-3s may also lower your risk of skin cancer. Regular consumption supports your skin’s natural defenses against harmful environmental factors.
Omega fatty acids are generally well-tolerated by all skin types. They’re considered gentle, hydrating ingredients with no known unwanted side effects, even if you have sensitive or reactive skin.
While combined omega-3-6-9 supplements are available, research suggests that focusing on omega-3 supplements alone may provide similar skin benefits. This is especially true if your diet already contains adequate omega-6 and omega-9 fatty acids.
Evolutionary Perspectives
Humans have dramatically changed their diets over millennia, shifting from balanced omega-6 to omega-3 ratios toward highly skewed proportions. These changes have important implications for our health today.
Dietary Changes Over Time
Early human diets contained roughly equal amounts of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids. Our Paleolithic ancestors consumed a diet with an omega-6 to omega-3 ratio of approximately 1:1. They obtained omega-3s from wild plants, seeds, and animals that fed on omega-3-rich vegetation.
This balanced intake supported optimal brain development and reduced inflammation. The evolutionary aspects of this diet align with how our bodies function best today.
Hunter-gatherer diets were characterized by:
- Lower total fat intake than modern diets
- Lower saturated fat consumption
- Balanced omega-6/omega-3 ratios
- Higher intake of plants and lean proteins
Your body evolved with these nutritional patterns over thousands of generations, making these fats essential for optimal health.
Modern Diet and Omega Intakes
Today’s typical Western diet has dramatically shifted to an omega-6/omega-3 ratio of 15:1 to 20:1, far from our evolutionary dietary pattern. This change happened primarily during the agricultural and industrial revolutions.
Your modern diet likely contains excess omega-6 fatty acids from:
- Processed vegetable oils (corn, safflower, sunflower)
- Factory-farmed meat from grain-fed animals
- Packaged and processed foods
These dietary changes have significant health implications. The increased omega-6/omega-3 ratio promotes inflammation, potentially contributing to chronic diseases including heart disease, diabetes, and autoimmune conditions.
You can counteract this imbalance by consuming more omega-3-rich foods like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, while reducing processed foods high in omega-6 fats.
Risks and Considerations
While omega fatty acids offer many health benefits, they come with potential risks that require careful consideration. Not all omega supplements are created equal, and certain medical conditions may warrant caution.
Potential Overconsumption
Excessive intake of omega fatty acids can lead to unwanted effects. Omega-3 fatty acids in high doses (more than 3 grams daily) may increase bleeding risk and potentially interfere with blood clotting. This is particularly important if you’re taking blood-thinning medications.
Too much omega-6 consumption without balancing omega-3s can promote inflammation in your body. The typical Western diet already contains excessive omega-6 fats, so additional supplementation may be unnecessary or even counterproductive.
Omega-9s are generally safe as they’re produced by your body, but excessive intake through supplements doesn’t offer additional benefits and may contribute to unnecessary calorie consumption.
Signs of potential toxicity from omega supplements may include:
- Fishy aftertaste or breath
- Digestive discomfort
- Nausea or bloating
- Loose stools
Interactions and Contraindications
Fish oil supplements can interact with certain medications. You should exercise caution if you take:
- Blood thinners (warfarin, aspirin)
- Blood pressure medications
- Birth control pills
Some medical conditions require careful consideration before starting omega supplements:
- Bleeding disorders: Omega-3s may increase bleeding risk
- Upcoming surgery: Stop supplementation 2 weeks before procedures
- Fish allergies: Choose algae-based alternatives if using omega-3 supplements
- Diabetes: Omega-3s may affect blood sugar in some people
If you’re pregnant or nursing, consult your healthcare provider before taking any omega supplements. Quality matters—choose products tested for contaminants like mercury and PCBs.
Future Directions in Research

Research on omega-3-6-9 fatty acids continues to evolve with exciting new directions. Scientists are exploring more precise ways to understand how these essential fats affect your health.
Cardiovascular disease prevention remains a key focus in omega-3 research. New studies are investigating optimal dosages and formulations to reduce heart risks. The ratio between omega-6 and omega-3 appears particularly important, as higher ratios may increase mortality risk.
Researchers are examining how omega fatty acids influence your gut microbiome. This emerging area may help explain the broader health impacts of these fats beyond direct cellular effects.
Important research directions include:
- Personalized nutrition approaches based on genetic profiles
- Long-term effects of different omega-3-6-9 ratios
- Development of enhanced delivery systems for better absorption
- Specific omega formulations for different health conditions
Neurodegenerative disease research is gaining momentum. Scientists are studying how omega-3s might protect your brain cells and potentially slow conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
The role of cytokines—inflammatory messaging molecules in your body—is another crucial area. Omega-3s appear to reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines while omega-6s can promote them in certain contexts.
Mendelian randomization studies represent a cutting-edge approach. These studies use genetic variations to better understand cause-and-effect relationships between omega fatty acids and disease outcomes.
Your optimal intake may depend on your individual health profile, genetics, and specific health goals. Future research will likely provide more personalized recommendations beyond current general guidelines.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the potential health benefits of taking Omega-3-6-9 supplements?
Omega-3 fatty acids are known to support heart health by reducing inflammation and lowering triglyceride levels. They may also help decrease joint pain and stiffness in people with arthritis.
Omega-3s are important for brain health and development. Some studies suggest they may improve symptoms of depression and ADHD in certain individuals.
Omega-6 fatty acids help with brain function and normal growth and development. However, most people already get plenty of omega-6 in their diets from cooking oils and processed foods.
Omega-9 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation and may improve insulin sensitivity. They’re also known to boost “good” HDL cholesterol while lowering “bad” LDL cholesterol.
How do Omega-3-6-9 fatty acids affect skin health?
Omega-3 fatty acids help maintain the skin’s natural oil barrier, keeping it hydrated and reducing acne. They can also protect your skin from sun damage and may reduce signs of aging.
Omega-6 fatty acids are crucial for skin health as they help maintain the skin barrier. However, too much omega-6 without enough omega-3 can increase inflammation, potentially worsening skin conditions.
Omega-9 fatty acids, like those found in olive oil, help improve skin elasticity and hydration. They can also protect against oxidative damage that leads to premature aging.
Together, a balanced intake of these fatty acids supports overall skin health by reducing inflammation and maintaining moisture and elasticity.
Can Omega-3-6-9 supplements have any side effects, and what are they?
High doses of omega-3 supplements (more than 3 grams daily) may cause digestive issues like nausea, diarrhea, or fishy breath. They can also thin your blood, potentially increasing bleeding risk.
Some people may experience allergic reactions to fish oil supplements, especially if they have seafood allergies. Plant-based omega-3 supplements might be a safer alternative for these individuals.
Omega-6 supplements rarely cause side effects when taken in appropriate amounts. However, excessive intake may promote inflammation when not balanced with enough omega-3s.
Omega-9 supplements are generally well-tolerated since your body can produce these fats naturally. Side effects are uncommon but might include digestive discomfort in some people.
What role do Omega-3-6-9 fatty acids play in weight management?
Omega-3 fatty acids may help with weight management by reducing inflammation and improving how your body responds to insulin. Some research suggests they might increase feelings of fullness after eating.
These fats might also help reduce belly fat specifically. Studies indicate omega-3s can boost metabolism slightly and help your body burn fat more efficiently during exercise.
The balance between omega-3 and omega-6 is important for weight control. The typical Western diet contains far more omega-6 than omega-3, which may contribute to weight gain through increased inflammation.
Omega-9 fatty acids found in olive oil may help reduce appetite and promote fat burning. Including these healthy fats in your diet can help you feel satisfied longer after meals.
How might Omega-3-6-9 fatty acid supplementation differ in benefits for men versus women?
Women may experience unique benefits from omega-3 fatty acids during pregnancy and menstruation. These fats are crucial for fetal brain development and can help reduce menstrual pain and mood symptoms.
Men might benefit from omega-3s’ positive effects on testosterone levels and reproductive health. Some studies suggest these fats can improve sperm quality and motility.
Both genders benefit from omega-3s’ heart-protective effects, but research indicates men might see more significant improvements in triglyceride levels and blood pressure.
Women going through menopause may find that omega fatty acids help manage symptoms like hot flashes and mood swings. These fats support hormonal balance during this transition.
What are the recommended dosages for Omega-3-6-9 supplements to ensure safety and efficacy?
For omega-3 fatty acids, most health organizations recommend 250-500 mg combined EPA and DHA daily for general health. Higher therapeutic doses (1-4 grams) may be recommended for specific conditions under medical supervision.
Most people don’t need omega-6 supplements since the typical diet already provides plenty. If supplementing, keep the amount lower than your omega-3 intake to maintain a healthy balance.
There are no official recommended doses for omega-9 supplements, as your body can produce these fats naturally. However, including sources like olive oil in your diet is beneficial.
Before starting any supplement regimen, consult with your healthcare provider. They can recommend appropriate dosages based on your specific health needs and medical history.
Conclusion
Omega-3, omega-6, and omega-9 fatty acids each play important roles in your health. Understanding their differences helps you make better dietary choices.
Omega-3 fatty acids are particularly valuable for your health. They’ve been linked to reduced risk of heart problems, including heart attacks and coronary heart disease.
Omega-6 fatty acids are essential but often consumed in excess in Western diets. Balancing your omega-3 to omega-6 ratio is key for optimal health benefits.
Omega-9 fatty acids, while beneficial, can be produced by your body, making them less critical to obtain from your diet compared to omega-3s and omega-6s.
For optimal health, focus on increasing omega-3 intake through fatty fish, flaxseeds, or high-quality supplements. Consider reducing omega-6 consumption from processed foods and vegetable oils.
The right balance between these fatty acids supports heart health, brain function, and helps manage inflammation in your body.
Quality matters when choosing supplements. Look for products that are third-party tested for purity and potency to ensure you’re getting the benefits you expect.
Remember that dietary changes should be discussed with your healthcare provider, especially if you have existing health conditions or take medications.