Salmon Oil vs Fish Oil: A Complete Nutritional & Benefit Guide
When you walk down the supplement aisle, you might wonder if salmon oil and fish oil are the same thing. While both provide omega-3 fatty acids, they come from different sources and offer distinct nutritional profiles that could impact your health goals.
Salmon oil contains higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids than most other fish oils, with salmon oil providing 4.25 grams of combined EPA and DHA per tablespoon compared to other fish oils that typically contain 1.4 to 2.95 grams. This difference affects everything from the price you pay to the health benefits you receive.
Understanding these differences will help you make the right choice for your budget and wellness needs. You’ll discover how each oil affects your heart health, brain function, and overall well-being, plus learn about potential risks and environmental considerations that might influence your decision.
What Are Salmon Oil and Fish Oil?
Both oils come from fish but differ in their sources and specific fish types used. Salmon oil is extracted from the tissues of salmon fish, while fish oil is derived from a variety of fish species.

Definition and Sources
Salmon oil comes specifically from salmon tissue. You get this oil only from salmon species, whether farmed salmon or wild-caught salmon varieties.
Fish oil uses multiple seafood sources. Fish oil is typically derived from various types of fish, giving manufacturers more flexibility in production.
The main difference is specificity. Salmon oil focuses on one type. Fish oil combines different species for broader omega-3 content.
Common fish oil sources include:
- Mackerel
- Sardines
- Anchovies
- Tuna
- Herring
Extraction Methods
Both oils use similar extraction processes. Manufacturers heat fish tissues to separate the oil from proteins and water.
Cold-pressing preserves more nutrients. This method uses lower temperatures to maintain omega-3 quality.
Heat extraction processes larger volumes faster. Higher temperatures can reduce some beneficial compounds but increase production efficiency.
Molecular distillation removes contaminants. This step purifies both salmon oil and fish oil by filtering out heavy metals and toxins.
Encapsulation creates supplements. Companies add the refined oil to soft gel capsules or bottles for consumer use.
Types of Fish Used
Salmon oil sources:
- Wild salmon from Alaska and Pacific waters
- Farmed salmon from aquaculture operations
- Atlantic and Pacific salmon varieties
Fish oil sources:
- Sardines: Small, nutrient-dense fish with high omega-3 content
- Mackerel: Oily fish with strong omega-3 profiles
- Anchovies: Tiny fish often used in bulk fish oil production
- Tuna: Larger fish providing substantial oil yields
Wild-caught salmon typically contains more omega-3s than farmed salmon. Smaller fish like sardines and anchovies often have fewer contaminants than larger species.
Fish oil contains more monounsaturated fats, and salmon oil is richer in polyunsaturated fats. The fish type directly affects the final oil composition you receive.
Key Differences Between Salmon Oil and Fish Oil
Salmon oil and fish oil differ significantly in their omega-3 content, with salmon oil containing higher levels of EPA and DHA. The fat composition varies considerably between these two supplements, affecting their nutritional benefits.

Omega-3 Fatty Acid Content
The most important difference between these oils lies in their omega-3 fatty acid levels. Salmon oil provides significantly more omega-3s than standard fish oil supplements.
Salmon oil contains:
- EPA: 13.023g per 100g
- DHA: 18.232g per 100g
- DPA: 2.991g per 100g
Fish oil contains:
- EPA: 6.273g per 100g
- DHA: 4.206g per 100g
- DPA: 0.619g per 100g
This means salmon oil delivers more than double the EPA content and over four times the DHA compared to standard fish oil. The higher omega-3 concentration makes salmon oil more potent for cardiovascular and brain health benefits.
EPA to DHA Ratio
The EPA to DHA ratio differs dramatically between these two oils. Salmon oil has a DHA-dominant profile with approximately a 1:1.4 EPA to DHA ratio.
Fish oil shows a more balanced but lower overall ratio of roughly 1.5:1 EPA to DHA. This difference matters because EPA primarily supports heart health and reduces inflammation, while DHA focuses on brain function and development.
Your choice should depend on your specific health goals. If you need more brain support, salmon oil’s higher DHA content works better. For general heart health, both oils provide benefits, but salmon oil delivers higher concentrations.
Other Nutritional Components
The fat composition varies significantly between salmon oil and fish oil beyond omega-3s.
Salmon oil contains:
- Polyunsaturated fat: 45%
- Monounsaturated fat: 30%
- Saturated fat: 22%
- Cholesterol: 485mg per 100g
Fish oil contains:
- Polyunsaturated fat: 17%
- Monounsaturated fat: 61%
- Saturated fat: 23%
- Cholesterol: 766mg per 100g
Fish oil has 281mg more cholesterol than salmon oil. Salmon oil also contains astaxanthin, a powerful antioxidant that gives salmon their pink color and provides additional anti-inflammatory benefits.
Neither oil contains meaningful amounts of vitamins, minerals, or other nutrients beyond fats.
Comparing Health Benefits
Both salmon oil and fish oil provide significant health advantages through their omega-3 fatty acid content. Salmon oil typically contains higher concentrations of EPA and DHA, while fish oil offers proven cardiovascular and anti-inflammatory benefits.
Heart Health
Your cardiovascular system benefits significantly from both salmon oil and fish oil supplements. Studies show that fish oil supplements reduce heart disease risk factors by lowering LDL cholesterol levels and increasing HDL cholesterol in your bloodstream.
Fish oil helps lower your triglyceride levels, especially if you have high blood lipids. Your blood pressure may also decrease when you take these supplements regularly.
Salmon oil contains almost 18% DHA and 10% EPA, making it particularly effective for heart health. Fish oil prevents plaque buildup on your artery walls, reducing your risk of developing heart disease.
Both oils support your cardiovascular health by improving cholesterol profiles. Your triglycerides can drop significantly with consistent use of either supplement.
Brain and Cognitive Function
Your brain requires omega-3 fatty acids for optimal function and development. DHA makes up a large portion of your brain tissue and supports cognitive processes throughout your life.
Salmon oil’s higher DHA content may provide superior brain health benefits compared to standard fish oil. Your cognitive function depends on adequate omega-3 intake, especially as you age.
During pregnancy, omega-3 supplements support your baby’s brain development. Children whose mothers took omega-3 supplements develop cognitive and motor skills more easily than those whose mothers didn’t use supplements.
Your memory and learning ability benefit from regular omega-3 intake. Both oils help protect against age-related cognitive decline by supporting brain cell health.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Your body’s inflammatory response decreases when you take fish oil or salmon oil regularly. These supplements help reduce chronic inflammation that can lead to serious health problems like diabetes and heart disease.
Salmon oil omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammatory compounds produced by your immune cells. Your joint pain may improve if you have rheumatoid arthritis.
Both oils provide anti-inflammatory benefits for your entire body. Your skin health improves as omega-3s protect against sun damage and support wound healing.
Joint health benefits from reduced inflammation in your connective tissues. You may experience less stiffness and improved mobility with regular supplementation.
Effects on Skin and Eye Health
Both salmon oil and fish oil provide omega-3 fatty acids that may benefit your skin and vision. The omega-3 content in these oils can help reduce inflammation and support healthy cell function in both areas.
Skin Health and Conditions
Salmon oil contains higher omega-3 concentrations than many other fish oils. This makes it potentially more effective for skin health.
Omega-3s may help with:
- Reducing skin inflammation
- Improving moisture retention
- Supporting skin barrier function
Fish oil supplements may benefit skin conditions like acne and eczema. The omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce redness and irritation.
Some studies show mixed results for acne treatment. While some people see improvements, others may experience worsening symptoms.
For eczema and psoriasis, omega-3s may help reduce dry, itchy skin. The anti-inflammatory properties can calm irritated areas.
Fish oil may also protect against sun damage. Research suggests it can reduce your skin’s sensitivity to UV rays.
Both oils work similarly for skin health. The main difference is salmon oil’s higher omega-3 content.
Eye Health
Omega-3 supplements may lower your risk of eye problems like glaucoma and age-related vision loss. Studies show promising results for eye protection.
The omega-3 fatty acids support healthy eye development. They play an important role in vision health throughout your life.
Eye benefits include:
- Reduced risk of macular degeneration
- Lower chance of dry eye syndrome
- Better overall eye function
Adequate omega-3 intake may benefit your eye health at any age. The fats help maintain proper eye structure and function.
Both salmon oil and regular fish oil provide these eye health benefits. The choice depends on your preference and omega-3 concentration needs.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
Both salmon oil and fish oil are generally safe when taken as directed. However, potential contamination risks and medication interactions require careful consideration before adding these supplements to your routine.

Contaminants and Heavy Metals
All fish oils carry some risk of contamination from pollutants in the ocean water. Salmon oil may contain small amounts of heavy metals and other toxins that fish absorb during their lifetime.
Common contaminants include:
- Mercury
- PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls)
- Dioxins
- Lead
Larger fish like salmon tend to accumulate more contaminants than smaller fish used in regular fish oil. This happens because they live longer and eat other contaminated fish.
Wild salmon generally contains fewer contaminants than farmed salmon. However, reputable supplement companies use purification processes to remove most harmful substances.
Choose brands that provide third-party testing results. Look for products that meet strict purity standards set by organizations like NSF International.
Oxidation is another concern with fish oils. Rancid oils can form harmful compounds and lose their beneficial properties. Store your supplements in cool, dark places and check expiration dates.
Interaction With Medications
Fish oils can interact with certain medications, especially blood thinners. High doses of fish oil supplements might increase bleeding risk and potentially raise stroke risk.
Medications that may interact include:
- Warfarin (Coumadin)
- Aspirin
- Clopidogrel (Plavix)
- Other anticoagulant drugs
Talk to your doctor before taking salmon oil or fish oil if you take blood-thinning medications. They may need to adjust your dosage or monitor your blood clotting time more closely.
People with fish allergies should avoid these supplements entirely. Even processed oils can trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
Start with lower doses to test your tolerance. Some people experience digestive issues like nausea, heartburn, or fishy burps when first taking omega-3 supplements.
Nutrient Composition Breakdown
Salmon oil contains 45% polyunsaturated fats, while fish oil provides 61% monounsaturated fats. Both oils differ significantly in their vitamin content and omega-3 fatty acid concentrations.
Fatty Acid Profiles
You’ll find major differences in fatty acid composition between these two oils. Salmon oil consists of 45% polyunsaturated fats, 30% monounsaturated fats, and 22% saturated fats.
Fish oil contains higher monounsaturated fat levels at 61% compared to salmon oil’s 30%. Salmon oil provides more polyunsaturated fats at 45% versus fish oil’s 17%.
Omega-3 Fatty Acid Content:
- EPA: Salmon oil contains 13.023g per 100g, fish oil has 6.273g
- DHA: Salmon oil provides 18.232g per 100g, fish oil offers 4.206g
- DPA: Salmon oil has 2.991g per 100g, fish oil contains 0.619g
Salmon oil is significantly richer in all types of omega-3 fatty acids. The total omega-3 content in salmon oil reaches over 34g per 100g.
Fish oil contains 281mg more cholesterol than salmon oil, providing 766mg per 100g compared to salmon oil’s 485mg.
Vitamin and Mineral Content
Both salmon oil and fish oil contain no measurable amounts of vitamins or minerals. These oils contain no amounts of proteins, carbohydrates, minerals, or vitamins.
You won’t find vitamin D, vitamin A, or other essential vitamins in either oil type. The nutrients come entirely from their fatty acid profiles.
Both oils provide identical calorie content at 902 calories per 100g. Your typical serving size of one tablespoon contains 123 calories from either oil.
The lack of vitamins and minerals means you’ll need to rely on other foods or supplements to meet your vitamin D, vitamin A, and mineral requirements. These oils serve primarily as concentrated sources of specific fatty acids rather than comprehensive nutrient providers.
Considerations for Choosing Between Salmon Oil and Fish Oil
Your choice between these supplements depends on your specific health goals, budget, and personal preferences. The omega-3 content, cost differences, and how well you tolerate each supplement will guide your decision.

Individual Nutritional Needs
Your omega-3 requirements should drive your supplement choice. Salmon oil contains up to 50% omega-3s per dose, making it more concentrated than regular fish oil.
Salmon oil provides higher levels of:
- EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid)
- DHA (docosahexaenoic acid)
- Additional antioxidants like astaxanthin
If you need maximum omega-3 benefits from fewer capsules, salmon oil offers better concentration. You can get the same nutritional value from fewer pills compared to standard fish oil supplements.
Fish oil provides more total omega-3s per dose in some cases. This makes it suitable if you have very high omega-3 needs or prefer taking larger amounts.
Consider your specific health goals when choosing. Both supplements support heart health, reduce inflammation, and benefit brain function.
Cost and Accessibility
Price differences between these supplements can impact your long-term use. Salmon oil costs more than fish oil, with average prices around $21.99 for 200 salmon oil capsules versus $9.99 for 180 fish oil capsules.
The higher cost of salmon oil reflects its concentrated omega-3 content and specialized sourcing. You pay more per bottle, but you may need fewer capsules daily.
Cost comparison factors:
- Initial bottle price
- Cost per serving
- Number of capsules needed daily
- Long-term supplement budget
Fish oil offers better value if you’re budget-conscious. Most grocery stores and pharmacies stock multiple fish oil brands, making it widely accessible.
Salmon oil requires shopping at specialty stores or online retailers. Limited availability can increase shipping costs and reduce your purchasing options.
Taste and Digestibility
Taste differences affect your ability to stick with supplementation long-term. Salmon oil usually does not taste fishy, while fish oil has a distinct, intense flavor.
Many people find salmon oil more palatable. This better taste profile reduces the likelihood of supplement discontinuation due to unpleasant aftertaste or burping.
Fish oil’s stronger taste can cause digestive discomfort in sensitive individuals. Some people experience fishy burps or nausea when taking standard fish oil supplements.
Digestibility factors to consider:
- Stomach sensitivity
- Previous reactions to fish supplements
- Timing of supplement intake with meals
- Capsule size preferences
Both supplements can cause side effects like headaches, diarrhea, or heartburn with excessive use. Start with lower doses to assess your tolerance before increasing intake amounts.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Both salmon oil and fish oil face significant environmental challenges related to overfishing and marine ecosystem disruption. The sustainability of your oil choice depends heavily on fishing methods and certification standards.
Fishing Practices and Overfishing
Nearly 90% of fisheries are overfished or exploited at maximum levels according to the UN Food and Agriculture Organization. This creates serious risks for both salmon oil and general fish oil production.
Fish oil typically comes from multiple fish species. This practice often leads to bycatch problems where non-target species get caught accidentally.
Wild-caught salmon face fewer bycatch issues since fishing targets specific salmon runs. However, wild salmon populations are declining in many regions due to overfishing pressure.
Key fishing sustainability concerns:
- Depletion of forage fish used in fish oil
- Disruption of marine food chains
- Accidental capture of dolphins, turtles, and other species
- Illegal fishing practices in unregulated waters
Your choice impacts these fishing pressures differently. Salmon oil from wild sources puts direct pressure on salmon stocks. Fish oil from multiple species spreads its impact across various marine populations.
Aquaculture and Certifications
About 70% of salmon are now farmed, with production expected to grow. Farmed salmon reduces pressure on wild stocks but creates new environmental challenges.
Farmed salmon requires fish meal and fish oil from wild-caught fish as feed. This means farmed salmon oil still depends on wild fish populations indirectly.
The Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) certifies sustainable fishing practices. Look for MSC-certified products when choosing either oil type.
Certification benefits:
- Verified sustainable fishing methods
- Traceability from ocean to bottle
- Protection of marine ecosystems
- Support for responsible fishing communities
Some fish oils use more eco-friendly fishing practices than others. Research shows alternatives like microalgae oil can supply omega-3s without marine ecosystem impact.
Your sustainability choice depends on checking certifications and understanding production methods for each specific product.
Alternatives and Related Supplements
Several marine and plant-based options provide omega-3 fatty acids beyond traditional salmon and fish oils. Krill oil offers unique benefits with better absorption, while algae-based supplements provide sustainable omega-3s without seafood.
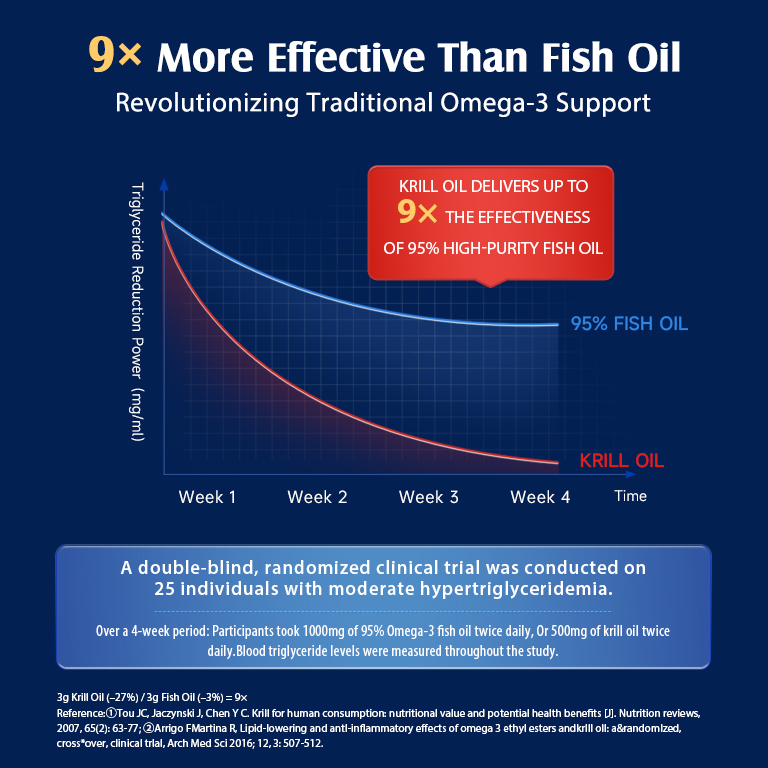
Krill Oil and Other Marine Oils
Krill oil comes from tiny shrimp-like creatures in Antarctic waters. It contains omega-3s in phospholipid form, which your body absorbs more easily than the triglyceride form found in fish oils.
Key advantages of krill oil:
- Better bioavailability than fish oils
- Contains astaxanthin, a powerful antioxidant
- Smaller capsule size
- Less fishy aftertaste
You typically need smaller doses of krill oil to get the same omega-3 benefits. However, krill oil costs more than regular fish oil supplements.
Other marine oils include squid oil and green-lipped mussel oil. Squid oil provides high DHA levels, making it useful for brain health. Green-lipped mussel oil contains unique omega-3s that may help with joint inflammation.
These alternative seafood sources offer different omega-3 profiles. Your choice depends on your specific health goals and budget.
Plant-Based Omega-3 Sources
Algae oil provides EPA and DHA without any seafood. Marine algae naturally produce these omega-3s, which fish then consume and store in their tissues.
Benefits of algae-based supplements:
- Suitable for vegetarians and vegans
- No mercury or ocean pollutants
- Sustainable production
- No fishy taste or burps
Algae oil typically costs more than fish oil but offers similar omega-3 content. Some products focus on DHA, while others provide both EPA and DHA.
Flaxseed oil and chia seed oil contain ALA omega-3s. Your body converts small amounts of ALA into EPA and DHA, but this process is inefficient. You would need much larger amounts to match the benefits of marine sources.
Walnuts, hemp seeds, and flax seeds provide whole food sources of plant-based omega-3s. These foods offer additional nutrients but lower omega-3 concentrations than concentrated oils.
Usage Recommendations and Dosage
Both salmon oil and fish oil have specific dosage guidelines based on your health goals and individual needs. Standard fish oil recommendations range from 1,000-2,000mg daily, while salmon oil typically requires lower doses due to its higher omega-3 concentration.
Optimal Daily Intake
Salmon Oil Dosage:
- General health: 500-1,000mg daily
- Heart health: 1,000-1,500mg daily
- Joint support: 1,000-2,000mg daily
Regular Fish Oil Dosage:
- General health: 1,000-2,000mg daily
- Cardiovascular support: 2,000-3,000mg daily
- Inflammation control: 2,000-4,000mg daily
Salmon oil contains approximately 1.5-2.5 grams of omega-3s per 1,000mg dose. This means you need less salmon oil to get the same EPA and DHA levels.
Important Timing Guidelines:
- Take with meals containing fat for better absorption
- Split larger doses throughout the day
- Morning intake may reduce evening digestive issues
There is no official recommended daily dosage for fish oil, but these ranges help you reach optimal omega-3 nutrient intake.
Who Should Supplement
Adults Who Benefit Most:
- People eating less than 2 servings of fatty fish weekly
- Those with heart disease risk factors
- Individuals with joint pain or inflammation
- Adults over 50 for cognitive support
Special Populations:
- Pregnant women: 200-300mg DHA daily
- Athletes: Higher doses for recovery (2,000-3,000mg)
- Vegetarians: Consider algae-based alternatives first
Medical Considerations: You should consult your doctor before supplementing if you take blood thinners. People with fish allergies should avoid fish-based oils entirely.
Age-Based Recommendations:
- Adults 18-50: Standard dosing
- Adults 50+: Focus on DHA for brain health benefits
- Children: Consult pediatrician for appropriate dosing
Start with lower doses and gradually increase to assess your tolerance and response.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the specific benefits of salmon oil over traditional fish oil?
Salmon oil contains astaxanthin, a powerful antioxidant that regular fish oil does not have. This compound gives salmon oil extra protection against cell damage.
You get higher omega-3 concentrations with salmon oil. Salmon oil typically has more beneficial compounds than generic fish oil made from multiple fish types.
The taste is often better with salmon oil. Some people find salmon oil more pleasant than standard fish oil, making it easier to take regularly.
Studies suggest that salmon oil may improve joint flexibility better than other fish oils. This makes it useful for people with joint problems.
How do salmon oil and cod liver oil differ in nutritional content and health benefits?
Cod liver oil contains high amounts of vitamins A and D, which salmon oil does not have. These vitamins support bone health and immune function.
Salmon oil has higher omega-3 levels than cod liver oil. It also contains astaxanthin for extra antioxidant benefits.
Cod liver oil works better for vitamin D deficiency. People in areas with little sunlight often benefit more from cod liver oil.
Salmon oil focuses on omega-3 benefits and inflammation control. Cod liver oil provides broader nutritional support through added vitamins.
Is there a difference in efficacy between fish oil and salmon oil for canine health?
Dogs often digest salmon oil better than generic fish oil. The single-source oil tends to cause fewer stomach problems in sensitive dogs.
Salmon oil provides better skin and coat benefits for dogs. The astaxanthin content helps create shinier fur and healthier skin.
Joint health improvements appear faster with salmon oil in dogs. Many pet owners report better mobility within a few weeks of use.
The taste appeal is usually higher with salmon oil. Dogs accept salmon oil supplements more readily than generic fish oil products.
What are the advantages of using krill oil compared to salmon oil and generic fish oil?
Krill oil absorbs better in your body than both salmon and fish oil. The phospholipid form allows easier uptake by your cells.
You need smaller doses of krill oil to get the same benefits. This makes krill oil more convenient despite higher upfront costs.
Krill oil causes fewer digestive issues than other options. Most people experience fewer fishy burps and stomach upset.
Krill oil contains astaxanthin like salmon oil, but in a more absorbable form. This provides better antioxidant protection than regular fish oil.
Which is more beneficial for feline health: salmon oil or fish oil?
Cats typically prefer the taste of salmon oil over mixed fish oils. This makes daily supplementation much easier for cat owners.
Salmon oil provides better skin benefits for cats with allergies. The anti-inflammatory properties help reduce itching and scratching.
Single-source salmon oil reduces the risk of food sensitivities in cats. Generic fish oil may contain proteins from multiple fish that trigger reactions.
Salmon oil supports better kidney function in older cats. The high-quality omega-3s help maintain healthy kidney filtration.
Are there any distinct benefits of salmon oil for heart health compared to other fish oils?
Salmon oil helps protect cardiovascular health by lowering cholesterol and blood pressure. The omega-3 content fights inflammation in blood vessels.
The astaxanthin in salmon oil provides extra heart protection. This antioxidant helps prevent damage to heart muscle cells.
Salmon oil outshines other fish oils in terms of omega-3 concentration per serving. Higher concentrations mean better heart health benefits.
Studies show salmon oil may reduce heart disease risk more effectively than generic fish oil. The combination of omega-3s and antioxidants works better together.
Conclusion
Both salmon oil and fish oil provide valuable omega-3 fatty acids for your health. The choice depends on your specific needs and budget.
Salmon oil offers these advantages:
- Higher concentrations of EPA and DHA
- Contains astaxanthin, a powerful antioxidant
- Better bioavailability for nutrient absorption
- Additional vitamins A and D
Fish oil provides these benefits:
- More affordable pricing
- Widely available options
- Still delivers essential omega-3s
- Good for basic supplementation needs
Your decision should consider several factors. If you want maximum omega-3 concentration and additional antioxidants, salmon oil is the better choice.
If cost is your main concern, regular fish oil still provides important health benefits. Both oils support heart health, brain function, and reduce inflammation.
Check the sustainability of your chosen product. Wild-caught salmon is generally more sustainable than many other fish sources.
Consider your tolerance for taste. Some people find that salmon oil has a more pleasant taste than standard fish oil.
Talk to your doctor before starting any supplement. They can help you choose the right type and dose for your health goals.
Both options will improve your omega-3 intake when taken regularly as part of a healthy diet.