18 Science-Based Omega-3 Benefits for Optimal Health.
Omega-3 fatty acids are powerful nutrients that can boost your health in many ways. These healthy fats support your heart, brain, and immune system. You can get omega-3s from foods like fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds.
Taking omega-3 supplements or eating omega-3-rich foods may help prevent and treat various health issues, including depression, anxiety, heart disease, and ADHD. These fats play a key role in how your body works, from muscle activity to cell growth.
Your body can’t make omega-3s on its own, so you need to get them from your diet. Eating fatty fish like salmon twice a week can help you get enough omega-3s. If you don’t eat fish, you can try plant sources or talk to your doctor about supplements.
Understanding Omega-3 Fatty Acids

Omega-3 fatty acids are key nutrients for your health. They come in different forms and can be found in various foods. These fats play a vital role in your body and offer many benefits.
Types of Omega-3s: ALA, EPA, and DHA
There are three main types of omega-3 fatty acids:
- Alpha-Linolenic Acid (ALA)
- Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA)
- Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA)
ALA is found in plant oils. Your body can’t make ALA, so you need to get it from food. EPA and DHA are mostly found in fish and other seafood. Your body can make small amounts of EPA and DHA from ALA, but it’s not very efficient.
Each type of omega-3 has unique roles in your body. DHA is crucial for brain health. EPA helps with heart health. ALA can be turned into EPA and DHA, but only in small amounts.
Sources of Omega-3s: Fish and Plant-Based Foods
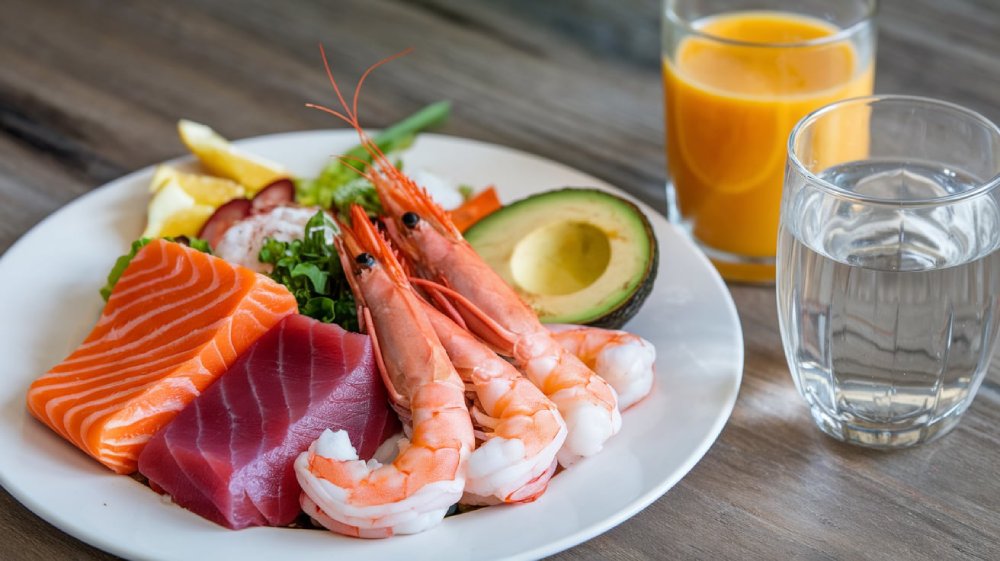

You can get omega-3s from both animal and plant sources. Fish is the best source of EPA and DHA. Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3s. It’s good to eat fish 1-2 times a week.
For plant-based sources, look for:
- Flaxseeds
- Chia seeds
- Walnuts
- Soybeans
- Canola oil
These foods are high in ALA. If you don’t eat fish, you might need to take EPA and DHA supplements made from algae.
Omega-3s vs Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Both omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids are types of polyunsaturated fats. Your body needs both but in the right balance. Most people eat too many omega-6s and not enough omega-3s.
Omega-6s are found in:
- Vegetable oils
- Nuts and seeds
- Meat and poultry
Too many omega-6s can lead to inflammation. Omega-3s help reduce inflammation. A good balance of omega-3s and omega-6s is key for your health.
Try to eat more omega-3-rich foods and less processed foods high in omega-6s. This can help improve your omega-3 to omega-6 ratio.
Cardiovascular Health and Omega-3s

Omega-3 fatty acids play a key role in heart health. They can help lower heart disease risk, improve blood fats, and regulate blood pressure. Let’s look at how omega-3s benefit your cardiovascular system.
Impact on Heart Disease and Stroke
Omega-3s may reduce your risk of heart disease and stroke. These fats can help prevent blood clots and lower inflammation in your arteries.
Studies show that omega-3s may cut your chances of dying from heart disease. They might also lower your risk of sudden cardiac death and atrial fibrillation.
For stroke prevention, omega-3s can reduce plaque buildup in arteries. This helps keep blood flowing smoothly to your brain. Aim to eat fatty fish twice a week or talk to your doctor about supplements.
Omega-3s and Blood Lipid Profiles
Omega-3 fatty acids can improve your blood lipid profile in several ways:
- Lower triglycerides
- Raise HDL (good) cholesterol
- Reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol particles
Research finds omega-3s significantly cut triglyceride levels. High triglycerides raise your risk of heart disease and stroke.
Omega-3s may also boost HDL cholesterol, which helps remove other forms of cholesterol from your bloodstream. This can improve your overall cholesterol balance and heart health.
Omega-3s and Blood Pressure Regulation
Omega-3 fatty acids can help regulate your blood pressure. They may lower both systolic and diastolic blood pressure in people with hypertension.
These effects seem strongest in those with untreated high blood pressure. Omega-3s work by:
- Reducing inflammation in blood vessels
- Improving blood vessel function
- Decreasing blood clotting
For best results, aim for 2-3 servings of fatty fish per week. You can also consider omega-3 supplements if you don’t eat much fish. Talk to your doctor about the right dosage for you.
Omega-3s and Brain Health
Omega-3 fatty acids play a crucial role in supporting brain health throughout life. These essential nutrients contribute to cognitive function, childhood development, and mental well-being.
Cognitive Function and Dementia
Omega-3s may help protect your brain as you age. Research suggests that these fatty acids could slow cognitive decline and reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. They support brain cell membranes and promote better communication between neurons.
Consuming omega-3s regularly might improve your memory and thinking skills. Some studies show that people who eat more fish or take omega-3 supplements perform better on cognitive tests.
For older adults, omega-3s may help maintain brain volume. This is important because brain shrinkage is linked to cognitive decline and dementia.
Childhood Developmental Benefits
Omega-3s are vital for brain development in infants and children. During pregnancy and early childhood, these nutrients help form the structure of the brain and eyes.
DHA, a type of omega-3, is especially important for fetal brain growth. It continues to support brain function throughout childhood and adolescence.
Children who get enough omega-3s may have:
- Better attention spans
- Improved learning abilities
- Enhanced problem-solving skills
For kids with ADHD, omega-3 supplements might help reduce symptoms like hyperactivity and inattention.
Mental Health Disorders
Omega-3s could play a role in managing mental health conditions. These fatty acids are part of brain cell membranes and affect neurotransmitter function.
Studies have shown that omega-3s might help with depression. People who eat more fish or take fish oil supplements often report fewer depressive symptoms.
Omega-3s may also benefit those with:
- Bipolar disorder
- Schizophrenia
- Anxiety disorders
While not a cure, adding omega-3s to your diet could be a helpful part of mental health treatment. Always talk to your doctor before starting any new supplement regimen.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Omega-3s
Omega-3 fatty acids have powerful effects on inflammation in your body. These healthy fats can help reduce chronic inflammation and may improve symptoms of certain autoimmune conditions.
Chronic Inflammation and Autoimmune Diseases
Omega-3s reduce the production of inflammatory substances in your body. This can be helpful for managing chronic inflammation, which is linked to many health problems.
Omega-3 fats may benefit autoimmune diseases like psoriasis and lupus. These conditions involve your immune system attacking healthy cells. By lowering inflammation, omega-3s could help ease symptoms.
Studies show that omega-3 supplements can decrease inflammatory markers in the blood. This suggests they may help control the overactive immune response in autoimmune disorders.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Joint Health
Omega-3 fatty acids can be especially beneficial for rheumatoid arthritis. This autoimmune disease causes painful joint inflammation.
Taking omega-3 supplements may reduce joint pain and stiffness. Some people are even able to lower their use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
Omega-3s can also help protect your joints. They may slow cartilage breakdown and reduce inflammation in the joint lining. This could help maintain joint health as you age.
For best results, aim for 2-3 grams of omega-3s daily. You can get this from fatty fish or high-quality fish oil supplements.
Omega-3s in Preventing and Managing Cancer

Omega-3 fatty acids may play a role in cancer prevention and management. These nutrients have shown promise in studies on various cancer types, including breast, prostate, and colon cancer.
Research on Breast and Prostate Cancer
Flaxseed consumption may help reduce tumor growth in breast and prostate cancer. Eating 25 grams daily could slow cancer progression. Flaxseed can also lower estrogen production, which may aid in breast cancer prevention.
Omega-3s might decrease inflammation and slow cancer cell growth. They can help maintain healthy cell membranes, potentially stopping cancer cells from spreading.
For prostate cancer, omega-3s may lower the risk of aggressive tumors. They could also help manage side effects of cancer treatments.
Colon Cancer and Omega-3s
Omega-3 fatty acids show potential in reducing colon cancer risk. They may improve immune response in patients undergoing colorectal cancer surgery.
These nutrients can help decrease inflammation in the colon. This effect may lower the chances of developing colon cancer or slow its progression.
Omega-3s might also help manage treatment side effects. For example, they can reduce the severity of nerve damage caused by certain chemotherapy drugs.
While more research is needed, including omega-3-rich foods in your diet may support colon health. Fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds are good sources to consider.
Eye Health and Omega-3s
Omega-3 fatty acids play a key role in eye health. They may help with dry eye symptoms and lower the risk of age-related eye problems.
Combating Dry Eye Disease
Dry eye disease can cause discomfort and vision issues. Omega-3 supplements may provide relief for some people with dry eyes. These fatty acids help produce oils that keep your eyes moist.
You can get omega-3s from fish or supplements. Good fish sources include:
- Salmon
- Sardines
- Tuna
- Herring
Taking omega-3 supplements might reduce dry eye symptoms in some cases. But results vary. Not everyone sees benefits from taking fish oil for dry eyes.
Your eye doctor can advise if omega-3s might help your dry eye symptoms. They may suggest trying supplements or eating more omega-3-rich foods.
Reducing the Risk of Macular Degeneration
Omega-3 fatty acids may help protect against age-related macular degeneration (AMD). AMD is a leading cause of vision loss in older adults.
A diet rich in omega-3s might lower your risk of developing AMD. These fatty acids support the health of your retina. They may also reduce inflammation in your eyes.
You can boost your omega-3 intake by:
- Eating fatty fish twice a week
- Adding flaxseeds or chia seeds to meals
- Using canola or soybean oil for cooking
While omega-3s show promise, they’re not a cure-all. A balanced diet and regular eye check-ups are still crucial for eye health.
Omega-3s and Metabolic Disorders
Omega-3 fatty acids play a key role in managing metabolic disorders. They can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation in the body.
Omega-3s in Managing Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome
Omega-3s may help improve blood sugar levels in people with metabolic syndrome. These fatty acids can increase insulin sensitivity, making it easier for your cells to use glucose.
For diabetes management, omega-3s can be beneficial. They may help lower triglyceride levels, which are often high in people with diabetes. Omega-3s also work to reduce inflammation, a common issue in metabolic disorders.
To get more omega-3s in your diet, try eating fatty fish like salmon or sardines twice a week. You can also take fish oil supplements but always talk to your doctor first.
Liver Health and Fat Reduction
Omega-3 fatty acids may help improve liver health in people with metabolic disorders. They can reduce liver fat, which is often high in those with metabolic syndrome.
Omega-3s can lower triglyceride levels in your blood and liver. This helps reduce the risk of fatty liver disease, a common problem in metabolic disorders.
Eating a diet rich in omega-3s or taking supplements may help decrease liver inflammation. This can improve overall liver function and health.
To boost your omega-3 intake, try adding flaxseeds or chia seeds to your meals. These plant-based sources are rich in alpha-linolenic acid, a type of omega-3.
Bone Health and Omega-3s
Omega-3 fatty acids play a key role in supporting bone health. These essential nutrients help maintain strong bones and may reduce the risk of bone-related issues as you age.
Benefits of Bone Strength and Development
Omega-3 fatty acids can improve bone strength by increasing calcium absorption in your bones. This helps make your skeleton more robust and less prone to fractures.
These healthy fats also have anti-inflammatory properties. By reducing inflammation in your body, omega-3s can help protect your bones from damage and support overall bone health.
Studies suggest that consuming omega-3s may:
- Enhance bone mineral density
- Reduce the risk of osteoporosis
- Improve bone formation
Research has shown that omega-3 fatty acids can help lower your risk of fractures. This is especially important as you get older and your bones naturally become more fragile.
To support your bone health, consider adding omega-3-rich foods to your diet. Good sources include:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- Flaxseeds
- Chia seeds
- Walnuts
By incorporating these foods into your meals, you can help maintain strong, healthy bones throughout your life.
The Role of Omega-3s in Respiratory Health

Omega-3 fatty acids play a key part in breathing health. They may help people with asthma and improve how well the lungs work.
Effects on Asthma and Lung Function
Higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids in the blood are linked to better lung health. These fats can slow down drops in lung function over time. This is good news for keeping your lungs strong as you age.
Omega-3s help fight swelling in the body. This can ease breathing in people with asthma. You may find it easier to breathe and have fewer asthma attacks.
Some studies show that omega-3s can boost how much air you can blow out. This is a sign of good lung health. Eating foods rich in omega-3s, like fish, might help your lungs stay healthy.
Asthma in Children and Dietary Intake
Kids with asthma may benefit from omega-3s too. Adding these fats to a child’s diet could help control asthma symptoms.
Research suggests that omega-3s might protect against lung problems. This could be helpful for children as their lungs grow and develop.
Eating fish or taking fish oil may lower the risk of asthma in kids. It’s important to talk to a doctor before changing a child’s diet. They can help you decide if adding more omega-3s is right for your child.
Dietary Guidelines and Omega-3 Intake
Getting the right amount of omega-3 fatty acids is key for your health. You need to balance your intake with other fats and be aware of seafood safety.
Recommended Omega-3 Dosage
The adequate intake of omega-3s varies by age and gender. For adults, aim for 1.1 to 1.6 grams per day. Pregnant women need slightly more. You can get omega-3s from food or supplements.
Fish oil supplements are a popular choice. They usually contain EPA and DHA. The dosage depends on your health goals. For general health, 250-500 mg of combined EPA and DHA daily is often suggested.
If you have heart issues, your doctor might recommend higher doses. Always talk to a healthcare provider before starting supplements.
Balancing Omega-6/Omega-3 Ratios
Your diet likely has too much omega-6 compared to omega-3. A good ratio is important for health. Experts suggest aiming for a 4:1 or lower ratio of omega-6 to omega-3.
To improve your ratio:
- Eat more omega-3-rich foods like fatty fish
- Use olive oil instead of vegetable oils
- Limit processed foods high in omega-6
Reducing vegetable oil intake can help boost your omega-3 status. This step is just as important as increasing omega-3s.
Seafood Consumption and Mercury Levels
Eating fish is great for omega-3s, but you need to watch out for mercury. Some fish have high mercury levels that can be harmful.
Low-mercury fish high in omega-3s include:
- Salmon
- Sardines
- Trout
- Anchovies
Aim for 2-3 servings of these fish per week. This gives you plenty of omega-3s without too much mercury risk.
Pregnant women and young children should be extra careful. They should avoid high-mercury fish like shark, swordfish, and king mackerel. Instead, they can choose safer options or talk to their doctor about omega-3 supplements.
Choosing and Using Omega-3 Supplements
Picking the right omega-3 supplement can be tricky. You’ll need to consider purity, freshness, and source. Different types of omega-3s offer unique benefits for your health and immune system.
Evaluating Purity and Freshness
When selecting omega-3 supplements, look for products that have been tested for purity. High-quality supplements should be free from contaminants like mercury and PCBs. Check the expiration date and smell the product – it shouldn’t have a strong fishy odor.
Omega-3 supplements often come from fish like mackerel, sardines, salmon, and tuna. These fish are rich in EPA and DHA, important types of omega-3s.
Some brands use molecular distillation to remove impurities. This process can help ensure a cleaner product. Look for supplements that list the amounts of EPA and DHA on the label.
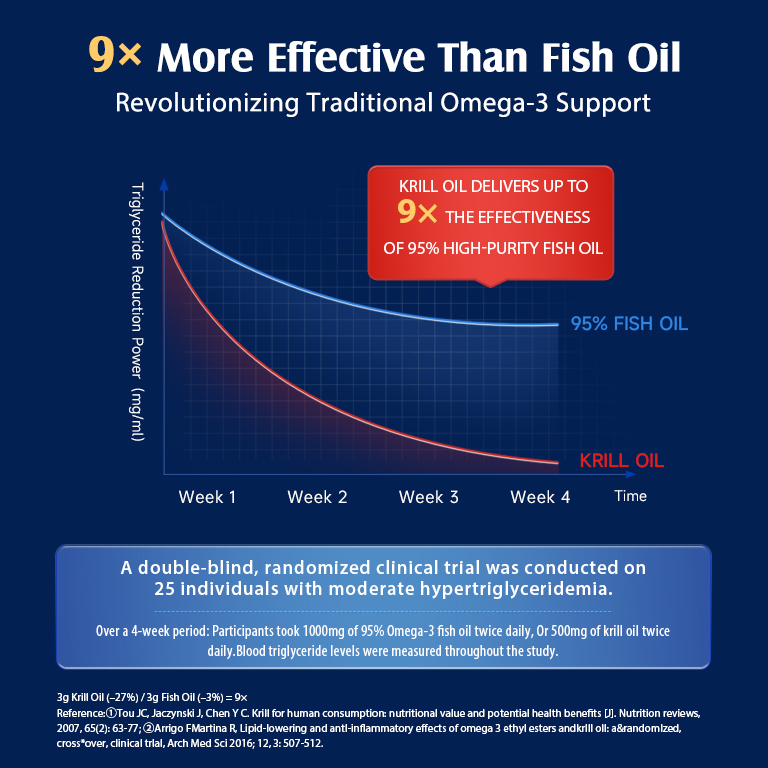
Fish Oil vs. Krill Oil and Algae Oil
Fish oil is the most common source of omega-3 supplements. It’s usually made from fatty fish like herring, anchovies, and sardines. Krill oil comes from tiny crustaceans and may be easier for your body to absorb.
Algae oil is a plant-based option that’s good for vegetarians and vegans. It provides DHA, one of the key omega-3s found in fish. Algae oil can be a good choice if you don’t eat fish or have concerns about ocean contaminants.
Cod liver oil is another option. It contains omega-3s plus vitamins A and D. But it may have too much vitamin A for some people.
Role of Omega-3s in Immune System Function
Omega-3 fatty acids play a key part in supporting your immune system. They help reduce inflammation in your body, which can boost immune function.
EPA and DHA, found in fish oil, may enhance the activity of white blood cells. These cells are crucial for fighting off infections. Omega-3s might also help your body produce antibodies.
Some studies suggest omega-3s could help with autoimmune conditions. They may calm overactive immune responses. However, more research is needed to fully understand these effects.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the significant advantages of incorporating Omega-3 in a daily diet?
Omega-3s are essential nutrients that can boost your overall health. They help reduce inflammation in your body and support heart health.
Omega-3s can improve your brain function and may lower your risk of certain chronic diseases. They also play a role in eye health and can help keep your skin looking healthy.
How do Omega-3 fatty acids impact cognitive health and brain function?
Omega-3s are crucial for your brain health. They help build and repair brain cells, which is important for memory and learning.
These fatty acids may also help protect your brain as you age. Some studies suggest that Omega-3s could lower your risk of cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease.
Can Omega-3 supplements significantly improve skin health, and if so, how?
Omega-3s can indeed benefit your skin health. They help keep your skin hydrated and may reduce acne and other skin problems.
These fatty acids can also protect your skin from sun damage and may help reduce signs of aging. By reducing inflammation, Omega-3s can contribute to a clearer, healthier-looking complexion.
What are the benefits of Omega-3 for maintaining heart health?
Omega-3s are great for your heart. They can help lower your blood pressure and reduce triglycerides, a type of fat in your blood.
These fatty acids may also decrease your risk of arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeats. Omega-3s can help prevent the buildup of plaque in your arteries, lowering your risk of heart disease.
In what ways do Omega-3 fatty acids affect joint health and inflammation?
Omega-3s have strong anti-inflammatory properties. This means they can help reduce joint pain and stiffness, especially in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
Regular intake of Omega-3s may improve your joint mobility and decrease your need for anti-inflammatory medications. They can also help protect your joints from further damage.
What role does Omega-3 play in hair growth and overall hair health?
Omega-3s can boost your hair health in several ways. They nourish hair follicles, which can lead to stronger, shinier hair.
These fatty acids may also help prevent hair loss and promote hair growth. By improving scalp health, Omega-3s can contribute to healthier hair overall.
Conclusion
Omega-3 fatty acids play a key role in your health. They can reduce inflammation and may help lower your risk of heart disease. These essential fats also support brain function and eye health.
Getting enough omega-3s in your diet is crucial. Fish, nuts, and seeds are good sources. For many people, a supplement can help fill the gap. NYO3 Omega-3 products are a high-quality option to boost your intake. Their pure formulas can help you get the omega-3s you need to support your well-being.