9 Omega-3 Fatty Acids Foods You Should Know.
Omega-3 fatty acids are vital for your health. They help your heart, brain, and body work well. You can find these good fats in many foods.
The best foods high in omega-3s are fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines. These fish give you lots of EPA and DHA, two key types of omega-3s. If you don’t eat fish, don’t worry. You can still get omega-3s from plant foods.
Some great plant sources of omega-3s are flax seeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. These foods have ALA, another type of omega-3. Your body can change some ALA into EPA and DHA. Adding these foods to your meals can boost your omega-3 intake and help you stay healthy.
The Importance of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids play crucial roles in your body and brain. These essential nutrients support your health in many ways, from protecting your heart to boosting your mood.
Overall Health Benefits
Omega-3s are important for your body and brain. Your body can’t make enough on its own, so you need to get them from food or supplements.
These fatty acids help reduce inflammation in your body. This can lower your risk of chronic diseases like arthritis and cancer.
Omega-3s also support eye health. They may help prevent age-related vision problems.
During pregnancy, omega-3s are vital for fetal development. They support the growth of your baby’s brain and eyes.
Cardiovascular Health
Omega-3 fatty acids are good for your heart. They can help lower your blood pressure and reduce triglycerides, a type of fat in your blood.
These nutrients may also slow the buildup of plaque in your arteries. This can lower your risk of heart disease and stroke.
Omega-3s can help prevent irregular heartbeats. They may reduce your risk of sudden cardiac death.
Eating foods rich in omega-3s or taking supplements may lower your risk of heart problems. This is especially true if you have a history of heart disease.
Cognitive Function and Mental Health
Omega-3s are crucial for brain health. They make up a large part of your brain’s cell membranes.
These fatty acids may help improve memory and thinking skills. Some studies suggest they might slow cognitive decline in older adults.
Omega-3s may also boost your mood. They’ve been linked to lower rates of depression and anxiety.
For children, omega-3s are important for brain development. They may help improve attention and reduce symptoms of ADHD.
Types of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids come in three main forms. Each type has unique properties and benefits for your health. Let’s explore the key differences between these essential nutrients.

ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid)
ALA is a plant-based omega-3 fatty acid. Your body can’t make it on its own, so you need to get it from food. Flax seeds, chia seeds, and walnuts are good sources of ALA.
This fatty acid helps with heart health and inflammation. Your body can convert some ALA into EPA and DHA, but the process isn’t very efficient.
To get enough ALA, try adding ground flax seeds to your oatmeal or yogurt. You can also use flaxseed oil in salad dressings.
EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid)
EPA is mainly found in fatty fish and seafood. It plays a big role in reducing inflammation in your body.
EPA can help with conditions like arthritis and heart disease. It may also improve your mood and mental health.
Good sources of EPA include:
- Salmon
- Sardines
- Mackerel
- Herring
Try to eat fish twice a week to boost your EPA intake. If you don’t like fish, consider taking a fish oil supplement.
DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid)
DHA is crucial for brain health and eye function. Like EPA, it’s mainly found in fatty fish.
Your brain contains high levels of DHA. It’s especially important during pregnancy and early childhood for proper brain development.
DHA may help:
- Improve memory
- Reduce the risk of age-related cognitive decline
- Support eye health
You can get DHA from fish sources similar to EPA. Algae-based supplements are also available if you follow a vegetarian or vegan diet.
Plant-Based Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids Foods
You can find omega-3 fatty acids in many plant-based foods. These options are great for vegans, vegetarians, or anyone looking to add more variety to their diet. Let’s explore some of the best plant sources of omega-3s.

Flaxseeds and Flaxseed Oil
Flaxseeds are tiny powerhouses of nutrition. They’re one of the richest plant sources of omega-3 fatty acids. Just one tablespoon of ground flaxseeds contains about 1.8 grams of omega-3s.
To get the most benefit, grind whole flaxseeds before eating. This helps your body absorb the nutrients better. You can sprinkle ground flaxseeds on cereal, or yogurt, or add them to smoothies.
Flaxseed oil is another option. It’s a concentrated source of omega-3s. Use it in salad dressings or drizzle it over cooked vegetables. Don’t use it for cooking, as heat can damage the delicate omega-3s.
Chia Seeds
Chia seeds are small but mighty. They’re packed with nutrients, including omega-3 fatty acids. One ounce of chia seeds provides about 5 grams of omega-3s.
These tiny seeds are versatile. You can add them to:
- Smoothies
- Yogurt
- Oatmeal
- Baked goods
Chia seeds absorb liquid and form a gel-like texture. This makes them great for making puddings or as an egg substitute in vegan baking.
Walnuts
Walnuts are a tasty and convenient way to get your omega-3s. They’re one of the best plant sources of these healthy fats. A handful of walnuts (about 1 ounce) contains 2.5 grams of omega-3s.
You can enjoy walnuts as a snack or add them to your meals. Try:
- Topping your salads with chopped walnuts
- Adding them to your morning cereal or oatmeal
- Using walnut oil in salad dressings
Walnuts also contain other nutrients like protein, fiber, and vitamin E. This makes them a nutritious addition to your diet.
Animal-Based Sources of Omega-3s
Fish and seafood provide the richest animal sources of omega-3 fatty acids. These foods contain high levels of EPA and DHA, which offer important health benefits. Let’s explore some key animal-based options for boosting your omega-3 intake.
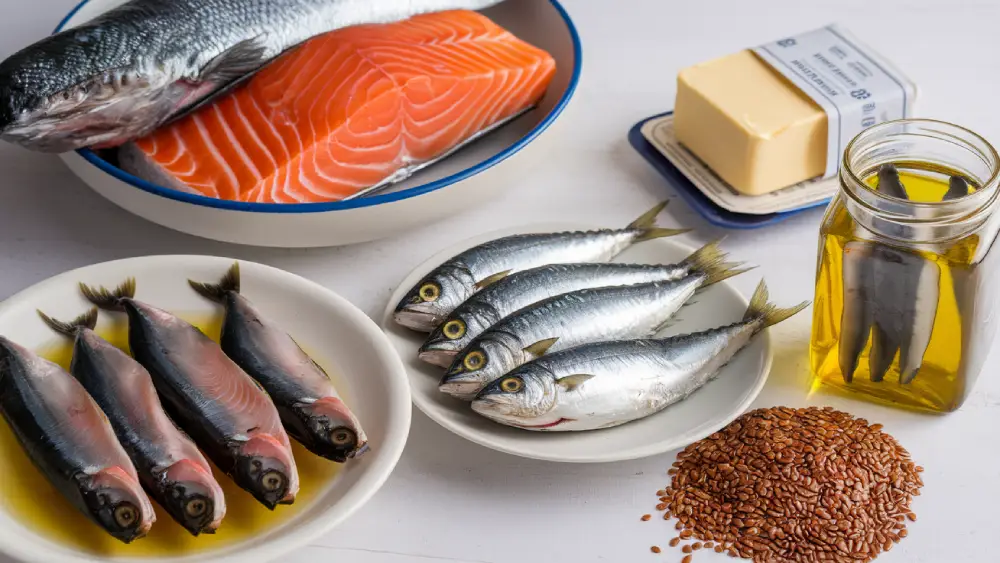

Fatty Fish Varieties
Fatty fish are the best source of omega-3s. Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and anchovies top the list. These fish contain high amounts of EPA and DHA. Aim to eat fatty fish 2-3 times per week.
Here are some fatty fish options and their omega-3 content per 3-ounce serving:
- Salmon: 1.8 grams
- Mackerel: 1.0 grams
- Sardines: 1.2 grams
- Anchovies: 1.4 grams
Tuna, herring, and trout are also good choices. You can grill, bake, or pan-fry these fish for easy meals. Add them to salads or sandwiches for a quick omega-3 boost.
Fish Oils
Fish oil supplements offer a concentrated dose of omega-3s. They’re made from the tissue of oily fish. Most fish oil supplements contain about 1,000 mg of fish oil per serving.
Look for supplements that list the EPA and DHA content. A typical 1,000 mg fish oil capsule contains:
- 180 mg EPA
- 120 mg DHA
Fish oil can help you meet your omega-3 needs if you don’t eat enough fatty fish. Talk to your doctor about the right dosage for you. Some people may need higher doses for specific health conditions.
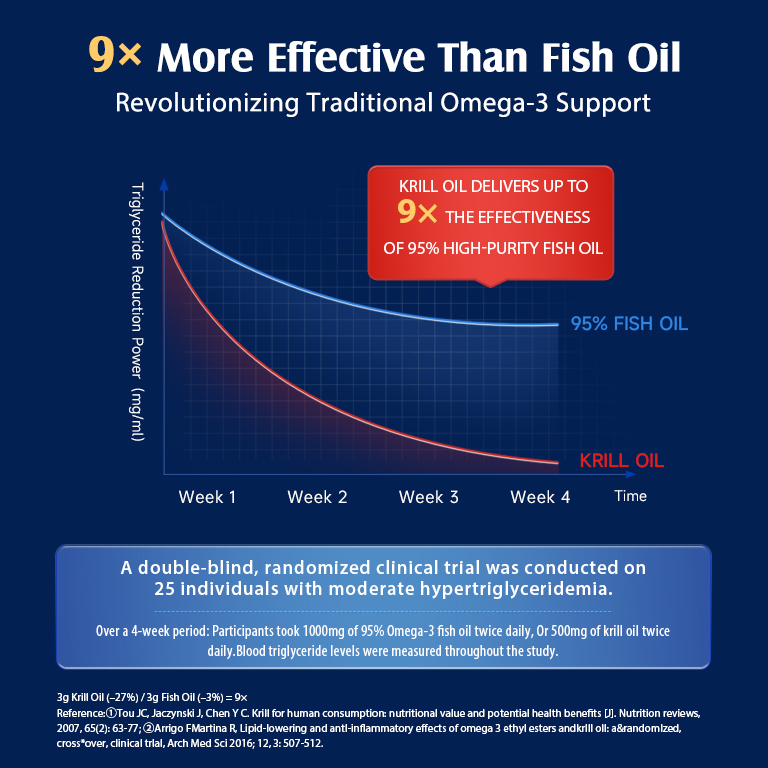
Krill Oil
Krill oil comes from tiny crustaceans called krill. It’s another rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA. Krill oil has a unique structure that may make it easier for your body to absorb.
Benefits of krill oil include:
- High antioxidant content
- It may be more easily absorbed than fish oil
- Less likely to cause fishy burps
Krill oil supplements typically contain less EPA and DHA per serving than fish oil. However, you may need a lower dose due to better absorption. As with fish oil, consult your doctor about the right amount for you.
Fortified Foods and Supplements
Some foods and supplements are specially made to have extra omega-3s. These options can help you get more of these healthy fats in your diet.

Omega-3 Enriched Eggs
Eggs can be enriched with omega-3 fatty acids. Farmers do this by feeding chickens a diet high in omega-3s. These eggs look and taste like regular eggs, but have more healthy fats.
You can find omega-3 eggs in most grocery stores. They’re often labeled as “omega-3 enriched” or “DHA eggs”. These eggs can have up to 5 times more omega-3s than standard eggs.
When you eat these eggs, you get more omega-3s without changing your usual meals. They’re great for breakfast or in baking.
Fortified Dairy and Juices
Many dairy products and juices are now fortified with omega-3s. You can find milk, yogurt, and orange juice with added DHA and EPA.
These fortified foods are an easy way to boost your omega-3 intake. They’re especially good for people who don’t eat fish often.
Check the labels when you shop. Look for words like “fortified with omega-3” or “DHA added”. The amount of omega-3s can vary between brands.
Remember, these foods aren’t as rich in omega-3s as fatty fish. But they can still help you get more of these healthy fats in your diet.
Omega-3 Supplements
If you don’t eat enough omega-3-rich foods, supplements can help. Fish oil capsules are a common choice. They contain both EPA and DHA.
You can also find algae-based supplements. These are good for vegetarians and vegans. They mainly provide DHA.
Omega-3 supplements come in different forms. You can get liquid oil, softgels, or gummies. The dose can vary, so check the label carefully.
Talk to your doctor before starting any supplement. They can help you decide if you need them and what dose is right for you.
Understanding Omega-3 Ratios and Dosages
Omega-3 fatty acids play a key role in your health. The main types are ALA, EPA, and DHA. Your body can’t make these on its own, so you need to get them from food or supplements.
A good balance of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids is important. The ideal ratio is between 1:1 and 4:1, but many people eat too much omega-6 fats compared to omega-3s.
To fix this, you can eat more omega-3-rich foods or take supplements. The right amount depends on your needs. Here are some general guidelines:
- For overall health: 250-500 mg of EPA and DHA per day
- For heart health: 1,000-4,000 mg per day
- For brain health: 1,000-2,000 mg per day
You can get omega-3s from foods like:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- Walnuts
- Flax seeds
- Chia seeds
If you choose supplements, look for ones with both EPA and DHA. Always talk to your doctor before starting any new supplement.
Remember, more isn’t always better. Very high doses can have side effects. Stick to the recommended amounts of 200-4,000 mg per day unless your doctor says otherwise.
The Role of Omega-3s in Special Diets
Omega-3 fatty acids play a crucial role in various dietary approaches. These essential fats can be incorporated into different eating patterns, each with unique considerations.
Vegan and Vegetarian Considerations
If you follow a vegan or vegetarian diet, you can still get omega-3s from plant sources. Nuts, seeds, and healthy oils are great options.
Flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts are rich in ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), a type of omega-3. Your body can convert ALA to EPA and DHA, but the process is not very efficient.
To boost your intake, try these tips:
- Add ground flaxseeds to smoothies or oatmeal
- Use chia seeds in puddings or as an egg substitute in baking
- Snack on walnuts or add them to salads
You might also consider algae-based supplements as a direct source of EPA and DHA.
Paleo Diet Compatibility
The Paleo diet aligns well with omega-3 intake. This eating plan emphasizes fatty fish, which are excellent sources of omega-3s.
You can easily incorporate these omega-3-rich foods into your Paleo meals:
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Sardines
- Anchovies
Grass-fed meat and pastured eggs also contain omega-3s, though in smaller amounts. These foods fit perfectly with Paleo principles.
For variety, you can include plant-based omega-3 sources like walnuts and flaxseeds. While some strict Paleo followers avoid these, many include them for their nutritional benefits.
Keto Diet and Omega-3s
The ketogenic diet, which is high in fat and low in carbs, can accommodate omega-3 fatty acids well. Fatty fish are both keto-friendly and rich in omega-3s.
You can easily fit these omega-3 sources into your keto meal plan:
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Sardines
- Fish oil supplements
Plant-based omega-3 sources like flaxseeds and chia seeds are also keto-compatible in moderation. They provide fiber along with omega-3s, but watch your portion sizes to stay within your carb limits.
Remember to balance your omega-3 intake with your overall fat consumption to maintain ketosis. Fish oil supplements can be a convenient way to boost your omega-3s without affecting your macronutrient ratios.
How to Incorporate Omega-3s into Your Diet
Eat more fish. Fish is a great source of omega-3s. Try to eat fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines two times a week.
Add nuts and seeds to your meals. Sprinkle walnuts on your oatmeal or add chia seeds to your smoothies. These foods are rich in plant-based omega-3s.
Use flaxseed oil in your cooking. Replace some of your regular cooking oils with flaxseed oil to boost your omega-3 intake.
Try omega-3-enriched eggs. Some hens are fed special diets to produce eggs with more omega-3s. Look for these at your grocery store.
Snack on edamame. These soybeans are a tasty way to get more omega-3s in your diet.
Consider a supplement. If you don’t eat fish, talk to your doctor about taking a fish oil supplement.
Here’s a quick list of omega-3-rich foods to include in your diet:
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Sardines
- Walnuts
- Chia seeds
- Flaxseeds
- Soybeans
Remember, your body can’t make omega-3s on its own. That’s why it’s important to include these foods in your diet regularly.
Omega-3 Deficiency and Overconsumption Risks
Not getting enough omega-3 fatty acids can lead to health problems. Worldwide deficiencies of omega-3s are common and raise the risk of chronic diseases.
Signs of omega-3 deficiency may include:
- Dry, itchy skin
- Brittle nails
- Poor sleep quality
- Joint pain or stiffness
- Difficulty concentrating
You can avoid deficiency by eating more omega-3-rich foods like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
While uncommon, taking too many omega-3 supplements can have side effects. These may include:
• Digestive discomfort • Fishy burps • Increased bleeding risk
To stay safe, don’t take more than 3 grams of omega-3s daily from supplements unless your doctor says it’s okay.
Eating fish is generally safe, but some types can have high mercury levels. Pregnant women and young children should limit certain fish.
Balance is key. Aim to get omega-3s from food first. If you take supplements, follow the dosage instructions on the label or from your doctor.
Interactions and Contradictions with Other Nutrients
Omega-3 fatty acids can interact with other nutrients in your body. These interactions may enhance or reduce their effects.
Omega-3 fatty acids and lutein work together to improve cognition. When combined, they can boost your memory, learning rate, and learning efficiency better than either nutrient alone.
Some nutrients may interfere with omega-3 absorption. High intake of omega-6 fatty acids can reduce the benefits of omega-3s. You should aim for a balanced ratio of these fats in your diet.
Vitamin E acts as an antioxidant for omega-3s, protecting them from oxidation. Including vitamin E-rich foods with your omega-3 sources can help preserve their effectiveness.
Omega-3s may also interact with certain medications. 76 drugs have moderate interactions with omega-3 supplements. If you’re taking any medications, consult your doctor before increasing your omega-3 intake.
Consider these potential interactions when planning your diet or supplement regimen. A balanced approach to nutrient intake can help you maximize the benefits of omega-3 fatty acids.
Latest Research on Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Scientists are making big strides in omega-3 research. Over 10,000 articles on the topic were published in 2019. The United States leads in this field, followed by China and Spain.
New studies look at omega-3s from different angles. They explore how these fats affect your health and where to get them.
Researchers are finding new ways to make omega-3s. They’re using plants and biotechnology. This could lead to more sources of these important fats.
Some key areas of recent omega-3 research include:
- Heart health
- Brain function
- Inflammation
- Immune system support
Omega-3s may help with COVID-19. They might lower inflammation and blood clot risk. This could be useful for treating the disease.
Scientists are also looking at omega-3s in yeast production. This could be a new way to make EPA and DHA. These are two important types of omega-3s.
As research continues, you can expect to learn more about how omega-3s affect your health. Keep an eye out for new findings and recommendations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the best natural sources of omega-3 fatty acids?
Fatty fish are excellent sources of omega-3s. Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and herring are top choices. Walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds also contain omega-3s. These plant-based options are rich in ALA, a type of omega-3.
Can I get enough omega-3 fatty acids from a vegetarian or vegan diet?
Yes, you can get omega-3s from plant sources. Flaxseeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, and walnuts are good options. Algae-based supplements are also available. These provide EPA and DHA, the types of omega-3s usually found in fish.
How does consuming omega-3 fatty acids benefit overall health?
Omega-3s support heart health by reducing inflammation and lowering triglycerides. They also promote brain function and may improve mood. These fatty acids are important for eye health and fetal development during pregnancy.
What are the differences between EPA, DHA, and ALA types of omega-3s?
EPA and DHA are found mainly in fish and algae. Your body uses these forms directly.
ALA comes from plant sources. Your body needs to convert ALA to EPA and DHA, but this process is not very efficient.
Are there any risks associated with consuming too much omega-3?
Excessive omega-3 intake can increase bleeding risk. This is especially important if you take blood-thinning medications. High doses may also lower your immune system function. It’s best to get omega-3s from food sources unless advised otherwise by your doctor.
How can I incorporate more omega-3 fatty acids into my diet without eating fish?
Add ground flaxseeds or chia seeds to your breakfast cereal or smoothies. Snack on walnuts or add them to salads. Use canola oil or flaxseed oil in cooking. Consider algae-based omega-3 supplements if you don’t eat any animal products.
Conclusion
Omega-3 fatty acids are vital for your health. You can find them in many tasty foods.
Fish is an excellent source. Salmon, mackerel, and sardines top the list. But if you don’t eat fish, don’t worry.
Plant-based options exist too. Flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts are great choices. You can easily add these to your meals.
Omega-3s may help your heart and brain. They might lower your risk of certain diseases. But more research is needed.
Remember to eat a variety of omega-3-rich foods. This ensures you get all types of omega-3s. Aim for at least two servings of fatty fish per week.
If you’re unsure about your intake, talk to a doctor. They can guide you on whether supplements are needed.
Incorporating omega-3 foods into your diet is simple. Start small and gradually increase. Your body will thank you for it.