Milk Thistle: Benefits, Uses, and Scientific Evidence
Milk thistle is a flowering herb with a long history as a natural remedy. Its active compound, silymarin, has caught the attention of researchers and health enthusiasts alike. You might have heard about this plant for its potential health benefits, especially for your liver.
Milk thistle supplements may help protect your liver from toxins, reduce inflammation, and support overall liver function. Studies suggest silymarin has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that could benefit people with various liver conditions. The herb has been used for centuries in traditional medicine systems before modern science began exploring its effects.
While research continues, many people take milk thistle as a dietary supplement for liver support, detoxification, and other health concerns. You should know that while this herbal remedy shows promise, not all claims about its benefits have strong scientific backing. Quality matters too—the concentration of silymarin varies between products, which can affect how well they work.
Historical Context and Origin
Milk thistle, also known as Mary thistle or holy thistle, has a fascinating history dating back thousands of years. This remarkable plant originated in Mediterranean countries and North Africa, where it thrived in the warm climate.
The plant’s distinctive appearance includes violet flowers and white-veined leaves. According to folk tradition, these white veins came from the Virgin Mary’s milk, which is how it earned the name “Mary thistle” or “holy thistle.”
Ancient Medical Applications
- Used for over 2,000 years in traditional medicine
- First documented in the 1st century by Greek physician Dioscorides
- Recommended for treating vomiting and as a nutritious food
When you look at the early records, you’ll find that Roman naturalist Pliny the Elder (23-79 AD) wrote about milk thistle’s juice and its virtues for “carrying of bile” – an early recognition of its liver-supporting properties.
The plant has been consistently valued throughout history. Its roots were often cooked with oil and salt as a tasty vegetable, showing that people appreciated both its medicinal and culinary uses.
By the time of the Middle Ages, milk thistle had become firmly established in European herbal medicine traditions. Healers would use different parts of the plant to address various ailments, particularly those related to liver and gallbladder functions.
Active Constituents of Milk Thistle
Milk thistle derives its therapeutic benefits from a unique complex of natural compounds found primarily in its seeds. These bioactive substances work together to provide the plant’s well-known liver-protective and antioxidant properties.
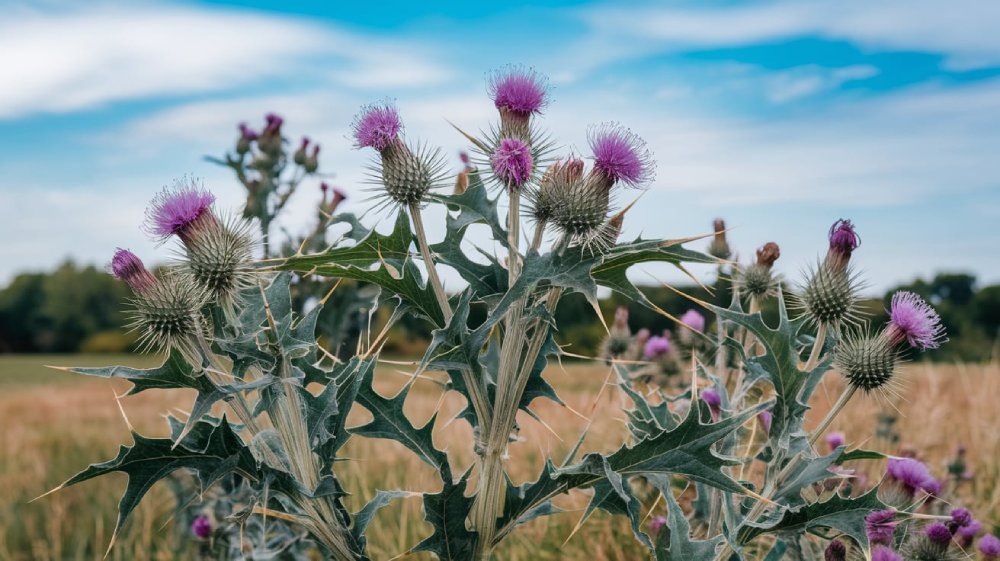

Silymarin and Its Components
Silymarin is the primary active compound in milk thistle, making up 65-80% of the extract from milk thistle seeds. This flavonolignan complex consists of several key components, including silybin (also called silibinin), silydianin, and silychristin. Among these, silybin is the most abundant and biologically active constituent.
Silybin accounts for about 50-70% of the silymarin complex and is considered the most powerful component responsible for milk thistle’s medicinal effects. When you take milk thistle supplements, you’re primarily benefiting from silybin’s properties.
The seeds also contain essential minerals like potassium, calcium, and phosphorus in trace amounts. These minerals complement the primary active constituents and contribute to the overall nutritional profile of milk thistle.
The Role of Antioxidants
The flavonoids in milk thistle function as powerful antioxidants in your body. They neutralize harmful free radicals and prevent oxidative damage to cells, particularly in the liver.
These antioxidant properties help protect your liver from damage caused by toxins, alcohol, and certain medications. Studies suggest that silymarin can reduce liver inflammation and may even help regenerate liver cells.
The antioxidant activity also explains why milk thistle is often recommended for people with various liver conditions. When you consume milk thistle, these compounds help:
- Stabilize cell membranes
- Inhibit inflammatory processes
- Scavenge free radicals
- Support enzyme production that neutralizes toxins
This protective mechanism makes milk thistle valuable for maintaining liver health and supporting detoxification processes in your body.
Milk Thistle in Liver Support
Milk thistle offers powerful protection for your liver through its active compound silymarin. This natural remedy has been used for centuries to treat various liver conditions and may help defend against toxins while supporting regeneration.
Protecting Against Liver Damage
Milk thistle contains silymarin, the primary active ingredient that helps shield your liver cells from harm. This powerful compound creates a protective barrier around liver cells, preventing toxins from entering and causing damage.
Research suggests milk thistle may be beneficial for people with various liver diseases, including alcoholic liver disease, fatty liver, and hepatitis. The herb works by reducing inflammation and blocking the effects of harmful substances.
When your liver processes alcohol or medications, it produces free radicals. Milk thistle acts as an antioxidant, neutralizing these damaging molecules before they can harm liver tissue.
For those with cirrhosis, milk thistle may help slow disease progression and improve liver function tests. However, results vary, and you should discuss using milk thistle with your doctor first.
Enhancing Liver Regeneration
Your liver has an amazing ability to repair itself, and milk thistle may enhance this natural regeneration process. Silybin, one specific flavonoid in milk thistle, provides up to 70% of the herb’s benefits to your liver and body.
Milk thistle stimulates protein synthesis in liver cells, which helps create new liver cells to replace damaged ones. This regenerative effect is particularly important if you have chronic liver conditions or have experienced liver damage.
When taken regularly, standardized milk thistle extracts (typically containing 70-80% silymarin) may:
- Accelerate liver cell renewal
- Reduce scarring in damaged liver tissue
- Support overall liver function
Some studies indicate milk thistle might help protect your liver from environmental toxins, making it potentially useful as a preventative supplement for those exposed to pollutants or chemicals.
Remember that while promising, milk thistle shouldn’t replace medical treatment for serious liver conditions. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
Clinical Benefits and Health Effects
Milk thistle offers several evidence-based health benefits beyond liver protection. Research shows promising results for metabolic health conditions and various inflammatory disorders.
Role in Managing Diabetes
Milk thistle may help people with diabetes manage their condition more effectively. Studies suggest that compounds in milk thistle can lower blood sugar in people with type 2 diabetes. This effect happens because silymarin, the active compound, may improve insulin sensitivity.
The plant contains a unique combination of antioxidants, fatty acids, and silymarin that work together to regulate insulin levels and maintain even blood sugar. This regulation can be particularly helpful if you’re at risk of developing diabetes or already managing the condition.
Research shows milk thistle might reduce the complications associated with diabetes by protecting cells from oxidative damage. However, you should note that more studies are needed to confirm these benefits and determine optimal dosing.
Impact on Cholesterol and Blood Sugar
Milk thistle’s beneficial effects extend to heart health markers including cholesterol and blood sugar levels. The herb contains high concentrations of beneficial fatty acids and omega-3s that support heart function and may help regulate cholesterol.
These compounds work to reduce inflammation throughout the body, which plays a key role in heart disease development. By lowering chronic inflammation, milk thistle may help protect your cardiovascular system.
For blood sugar management, silymarin appears to improve cellular sensitivity to insulin. This improved sensitivity helps your body process glucose more efficiently, potentially leading to better long-term blood sugar control.
Clinical studies show varying results, indicating that individual responses may differ. While milk thistle shows promise for these conditions, you should discuss it with your healthcare provider before using it as a treatment.
Potential Side Effects and Allergies
While milk thistle is generally considered safe for most people, it can cause adverse reactions in some individuals. Those with specific allergies should exercise caution before taking this supplement.
Common Adverse Reactions
Milk thistle may cause digestive discomfort in some users. The most frequently reported issues include diarrhea, bloating, gas, and upset stomach. These symptoms typically occur when you first start taking the supplement or if you take higher doses than recommended.
Nausea is another common side effect that you might experience. Most of these gastrointestinal issues are mild and temporary, often resolving as your body adjusts to the supplement.
It’s worth noting that when taken in appropriate doses, oral use of milk thistle appears to be safe for most people. If you experience persistent or severe symptoms, you should discontinue use and consult with your healthcare provider.
Identifying Allergic Responses
Some people may develop allergic reactions to milk thistle. You’re at higher risk if you have existing allergies to plants in the same family, including:
- Artichokes
- Ragweed
- Daisies
- Marigolds
- Chrysanthemums
- Kiwi
Signs of an allergic reaction may include skin rashes, itching, or hives. In rare cases, milk thistle can cause severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis), which is a medical emergency.
Watch for symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, and dizziness. If you experience these symptoms after taking milk thistle, seek immediate medical attention. To prevent allergic reactions, consider a small test dose before regular use.
Usage and Dosage Recommendations
Taking milk thistle correctly requires knowledge of both the available forms and appropriate dosages. Proper usage can maximize the potential benefits for your liver health and other conditions.

Forms of Milk Thistle
Milk thistle is available in several forms to suit different preferences and needs. Capsules and tablets are the most common and convenient options, offering precise dosing and easy storage. These typically contain standardized milk thistle extract with 70-80% silymarin, the active compound.
Liquid extracts and tinctures provide an alternative for those who have difficulty swallowing pills. You can add these to water or juice to mask the bitter taste.
Milk thistle tea is a gentler option, though it contains lower concentrations of silymarin than supplements. To prepare, steep 1-2 teaspoons of crushed seeds in hot water for 10-15 minutes.
Some health stores also offer milk thistle powder, which you can mix into smoothies or foods.
Determining the Optimal Dosage
The right milk thistle dosage depends on your health goals and condition. For general liver support, 140-800 mg daily of standardized extract containing 70-80% silymarin is typically recommended.
Specific conditions may require tailored dosages:
| Condition | Recommended Daily Dosage |
| Liver Health | 200-400 mg divided in 2-3 doses |
| Diabetes | 420-600 mg |
| Digestive Support | 150-300 mg |
Start with a lower dose and gradually increase it while monitoring for any side effects. Most people tolerate milk thistle well, but mild digestive discomfort occasionally occurs.
Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting milk thistle, especially if you take medications or have existing health conditions. The supplement may interact with certain drugs that are processed by the liver.
Interactions with Medications
Milk thistle may interact with several medications you take, affecting how they work in your body. The herb can influence cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are responsible for metabolizing many drugs.
Be cautious when taking milk thistle with blood-thinning medications. The combination may increase your risk of bleeding. Always talk to your doctor before combining these substances.
If you take diabetes medications, be aware that milk thistle might lower your blood sugar levels. You should monitor your blood sugar closely and consult your healthcare provider before starting milk thistle supplements.
Milk thistle may also interact with the medication raloxifene (Evista), which is used to prevent osteoporosis in postmenopausal women.
There are 4 known drug interactions with milk thistle, including:
- 3 moderate interactions
- 1 minor interaction
The good news is that milk thistle appears to have a relatively low risk of drug interactions compared to many other herbs.
Important precautions:
- Tell your doctor about all the supplements you take
- Don’t stop prescription medications without medical advice
- Watch for unusual side effects when combining milk thistle with pharmaceuticals
Current Research and Future Prospects
Scientific investigation into milk thistle continues to evolve with promising discoveries about its therapeutic applications. Researchers are exploring its benefits beyond traditional liver protection, with exciting developments in neurological conditions and cancer treatment.

Emerging Studies on Milk Thistle
Recent research has revealed milk thistle may have potential efficacy against COVID-19, expanding its known antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. This has contributed to increased demand for milk thistle supplements.
Studies are investigating silymarin’s role in protecting against cognitive decline. The compound shows neuroprotective effects that might benefit conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease by reducing oxidative stress in brain cells.
Research is also uncovering a two-phase process in how milk thistle works. Scientists have found it first activates stress response pathways, then later suppresses inflammation—giving it unique therapeutic potential.
Potential for Novel Therapeutic Uses
Clinical trials are examining milk thistle’s applications for cancer treatment. Patent formulations combining milk thistle with other natural extracts have shown promise in improving liver function and potentially addressing liver cancer.
You might be interested to know that milk thistle is being studied for eye diseases. Researchers are evaluating its therapeutic effects in treating various ophthalmological conditions through its pharmacological activities.
Future studies will likely focus on:
- Optimal dosing protocols
- Combination therapies
- Enhanced bioavailability
- Specific mechanisms of action
The continued genetic and genomic study of milk thistle may unlock new compounds with even greater therapeutic potential than currently known.
Milk Thistle in Traditional and Alternative Medicine
Milk thistle has been valued for its medicinal properties for over 2,000 years across different healing traditions. This remarkable herb contains powerful compounds that have made it a staple in both historical treatments and modern alternative approaches.
Historical Uses
Milk thistle’s therapeutic use dates back to ancient times when it was recognized for its remarkable healing potential. In the 1st century, military physician Pedanios Dioskurides recommended the root of the plant with honey as a remedy for vomiting. He also noted that cooking the root with oil and salt created a tasty vegetable dish.
The plant gained prominence in traditional medicine primarily for liver support and detoxification. Early healers observed its effectiveness for:
- Treating liver disorders
- Supporting digestive health
- Addressing gallbladder problems
- Protecting against poisonous snake bites
Throughout European folk medicine, milk thistle was commonly used to stimulate milk production in nursing mothers (hence its name). Traditional practitioners valued its purifying properties, often prescribing it for cleansing the blood and supporting overall wellness.
Contemporary Herbal Practices
Today, milk thistle remains one of the most researched herbs in alternative medicine, primarily recognized for its liver-protective effects. Modern herbal practitioners recommend it for various health concerns beyond liver support.
The active compound in milk thistle, silymarin, is a complex of flavonoids and antioxidants that shield liver cells from damage. This makes it popular for:
- Supporting liver function after alcohol consumption
- Complementing treatments for fatty liver disease
- Aiding detoxification protocols
Research suggests milk thistle, when combined with traditional treatments, can improve diabetes management by decreasing blood sugar levels and improving cholesterol profiles. You might find it in various forms including capsules, tinctures, and teas.
Herbalists often recommend milk thistle as part of holistic protocols for skin conditions, hormone balance, and cognitive health. Its powerful antioxidant properties make it valuable for protecting brain function and supporting overall wellness in complementary medicine approaches.
The Role of Milk Thistle in Nutrition and Diet
Milk thistle offers more than just medicinal benefits. It contains valuable nutrients and compounds that can complement a balanced diet while supporting overall wellness.

Nutritional Profile
Milk thistle seeds are the most nutrient-dense part of the plant. They contain essential vitamins, minerals, and bioactive compounds. The star component is silymarin, a flavonoid complex responsible for many of milk thistle’s health properties.
Other nutrients in milk thistle include:
- Vitamin E: An important antioxidant
- Fatty acids: Including omega-3 fatty acids
- Protein: Small amounts of plant protein
- Fiber: Supports digestive health
The primary active compound, silymarin, makes up about 70-80% of the extract from milk thistle seeds. This compound is known for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Incorporating into a Healthy Diet
You can add milk thistle to your diet in several forms. The most common is as a supplement in tablets, capsules, or liquid extract.
Some practical ways to use milk thistle:
- Tea: Steep dried milk thistle leaves in hot water
- Powder: Add to smoothies or sprinkle on food
- Seeds: Grind and add to salads or baked goods
When choosing supplements, look for products standardized to contain 70-80% silymarin for maximum benefit. Start with lower doses and increase gradually as your body adjusts.
Remember that milk thistle supplements should complement, not replace, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole foods.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the potential benefits of taking milk thistle for the liver?
Milk thistle contains silymarin, a compound that helps protect liver cells from toxins. This protective effect can support liver function and promote cell repair.
Research shows milk thistle may help people with liver diseases like hepatitis and cirrhosis. It works by reducing inflammation and preventing the buildup of harmful substances.
For those with fatty liver disease, milk thistle might slow progression and improve liver enzyme levels. However, more studies are needed to confirm these benefits.
Can milk thistle assist in detoxifying the liver, and if so, for what duration should it be taken?
Yes, milk thistle can support your body’s natural detoxification processes by enhancing liver function. It helps remove toxins and promote the regeneration of liver tissue.
Most experts recommend taking milk thistle for 3-6 months to see benefits for liver health. For maintenance, some people take it for 8-12 weeks followed by a break.
Your specific needs may vary based on your health condition. Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the right duration for your situation.
Are there any risks or side effects associated with consuming milk thistle supplements?
Milk thistle can cause digestive issues like nausea, bloating, and diarrhea in some people. These effects are usually mild and temporary.
Some users may experience allergic reactions, especially those with allergies to plants in the same family (ragweed, chrysanthemums, marigolds, daisies).
Milk thistle may interact with certain medications, including those processed by the liver. Always talk to your doctor before starting supplements, especially if you take other medications.
How might milk thistle influence the treatment or prevention of cancer?
Laboratory studies suggest silymarin in milk thistle may have anti-cancer properties by slowing cell growth and increasing cell death in cancer cells. However, human studies are limited.
Some research indicates milk thistle might help reduce the side effects of cancer treatments. It may protect healthy cells while allowing treatments to target cancer cells.
While promising, current evidence isn’t strong enough to recommend milk thistle as a cancer treatment. More clinical trials are needed to understand its full potential.
What specific advantages does milk thistle offer to women’s health?
Milk thistle may help manage hormonal balance by supporting liver function, which plays a role in processing hormones. This could benefit women experiencing menopause symptoms.
Some women report improvements in acne and other skin conditions when taking milk thistle due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Research also suggests milk thistle might support breast health, though more studies are needed in this area.
In what forms is milk thistle available and how should it be used for maximum efficacy?
Milk thistle is available as capsules, tablets, tinctures, and liquid extracts. Standardized extracts containing 70-80% silymarin are considered most effective.
For best absorption, take milk thistle with meals rather than on an empty stomach. The recommended dosage typically ranges from 140-800 mg daily, divided into 2-3 doses.
Milk thistle tea is another option, though it contains less silymarin than extracts. Some people add ground milk thistle seeds to foods or smoothies for a natural approach.
Conclusion
Milk thistle offers impressive health benefits for your body. The herb’s active compound, silymarin, works as a powerful antioxidant that protects cells from damage.
Your liver gains the most from milk thistle. It supports liver detoxification and regeneration, making it helpful for people with fatty liver disease or those taking medications like statins.
Beyond liver health, milk thistle may improve your heart function and help regulate blood sugar levels. Some research suggests it could even boost cognitive function.
For best results, take milk thistle with food for optimal absorption. This simple step helps your body use the herb more effectively.
While research confirms many traditional uses of milk thistle, especially for liver support, more human studies would strengthen our understanding of all its benefits.
Consider adding milk thistle to your wellness routine if you’re looking for natural support for your liver, skin health, or overall well-being. It represents a time-tested herbal remedy with science backing many of its traditional uses.